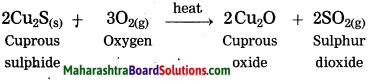
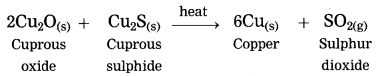
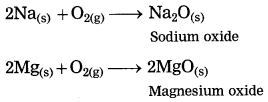
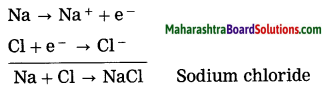
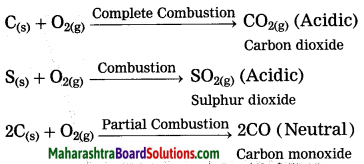
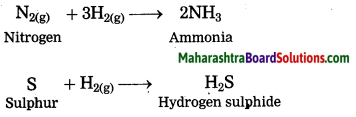
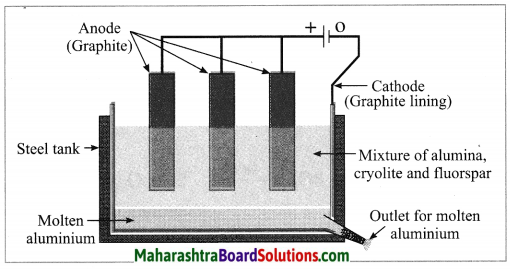
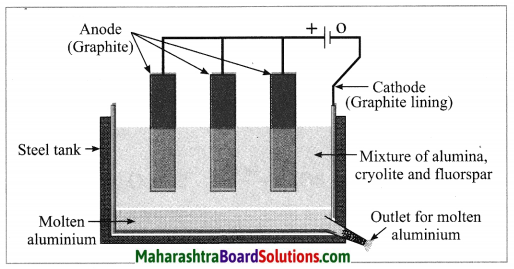
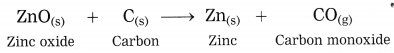
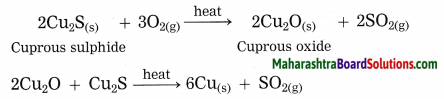
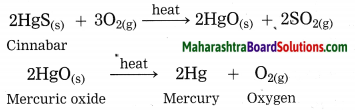
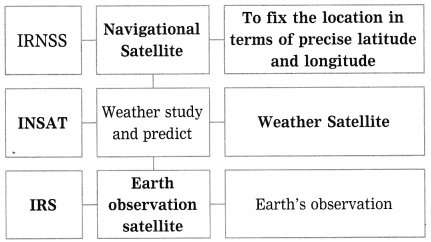
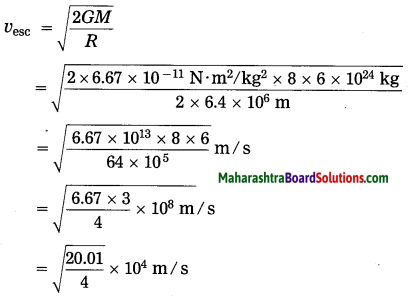
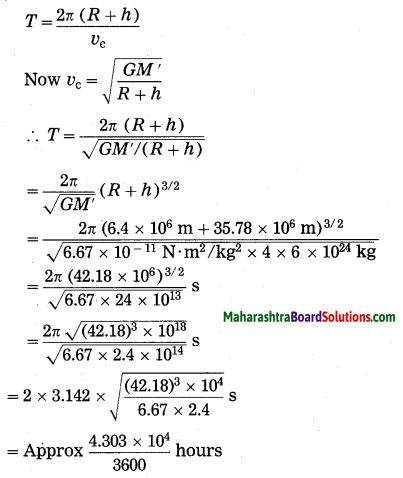
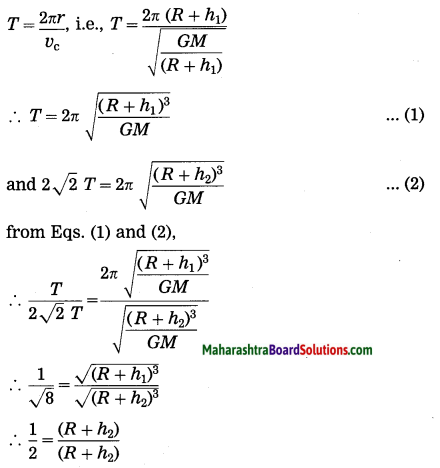
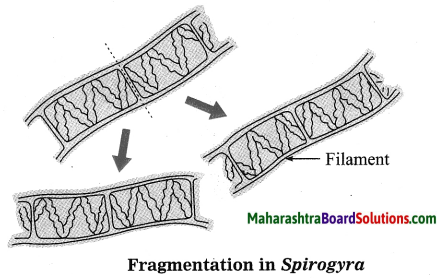
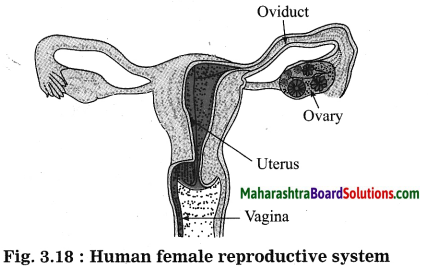
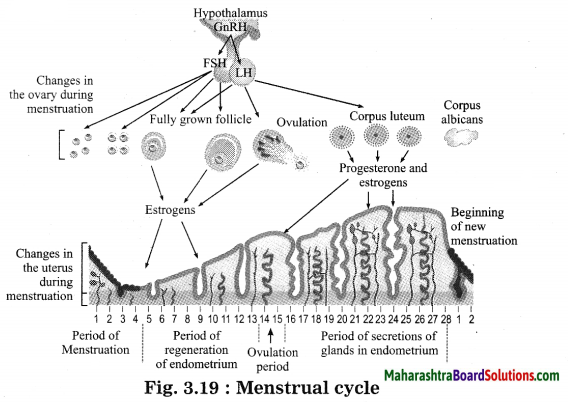
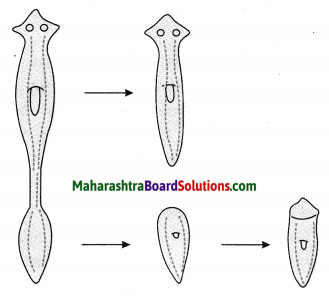
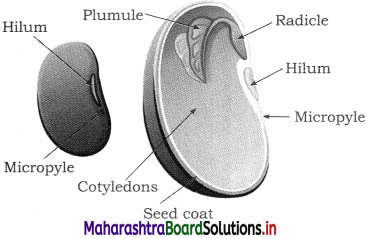
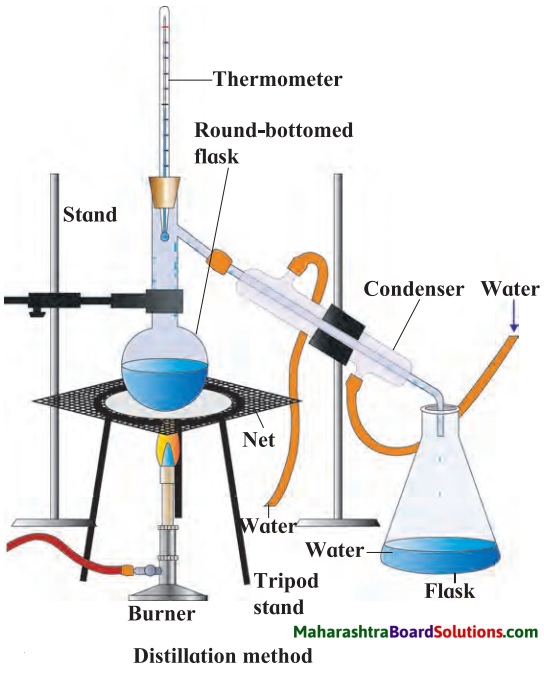
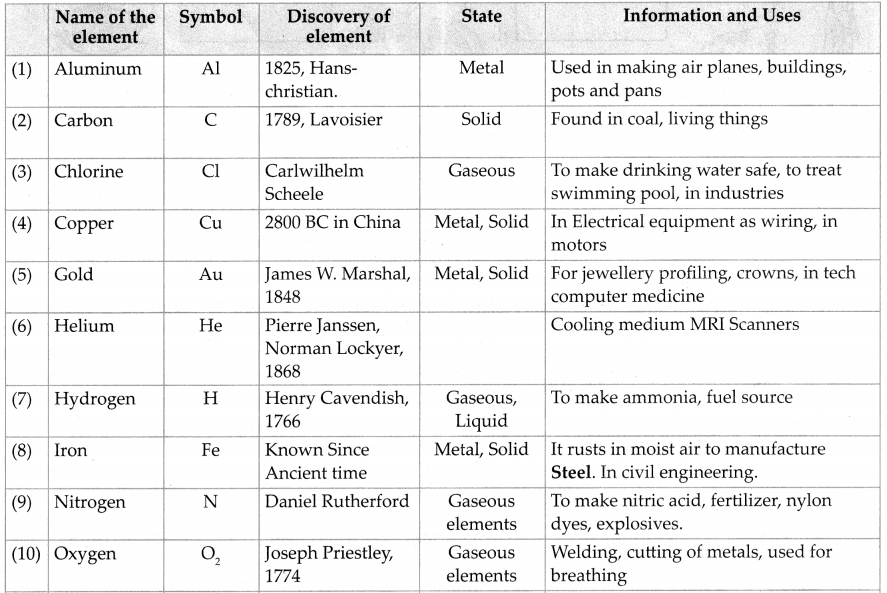
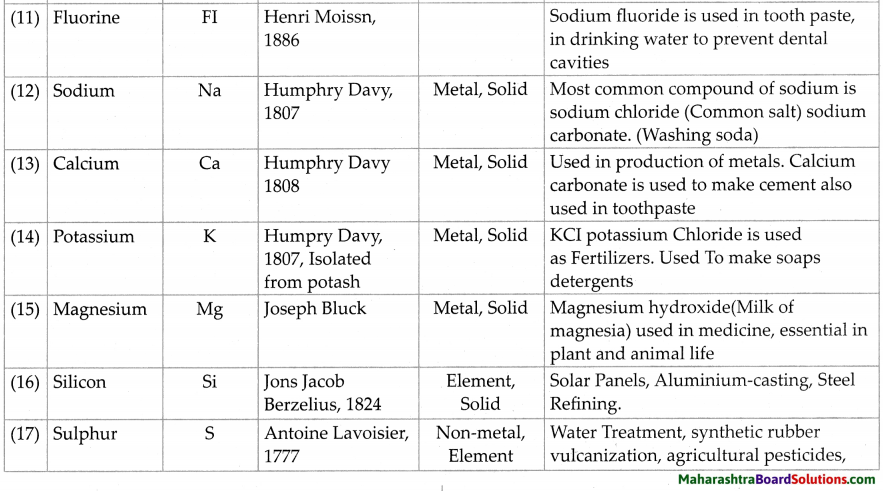
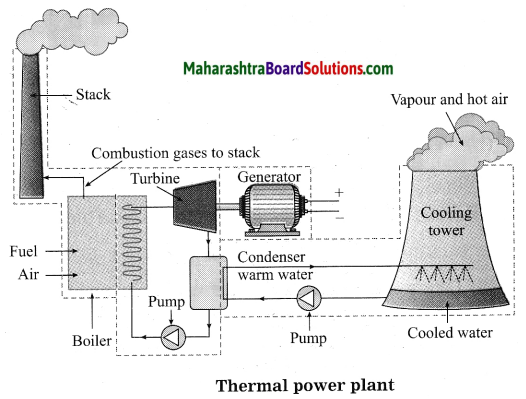
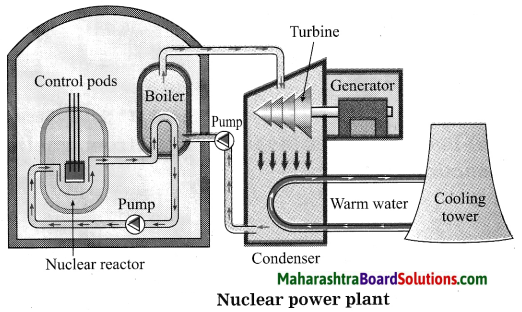
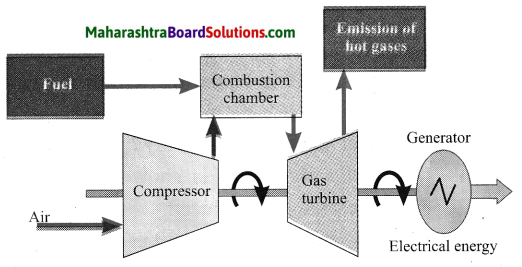
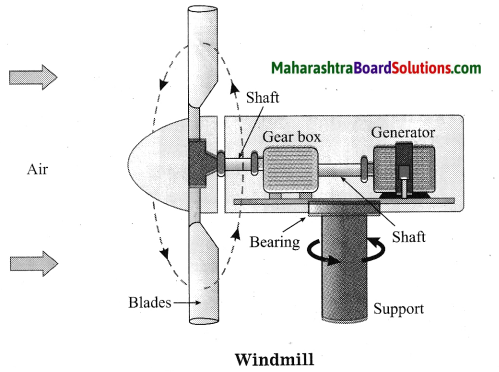
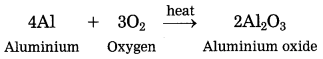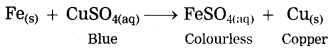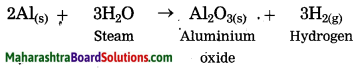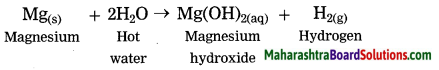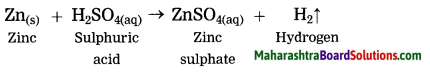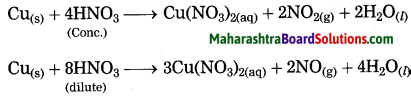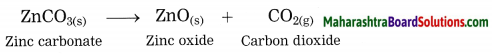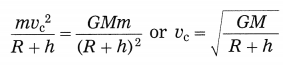Units and Measurements Class 11 Exercise Question Answers Solutions Maharashtra Board
Balbharti Maharashtra State Board 11th Physics Textbook Solutions Chapter 1 Units and Measurements Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 Exercise Solutions Maharashtra Board
Physics Class 11 Chapter 1 Exercise Solutions
1. Choose the correct option.
Question 1.
[L1M1T-2] is the dimensional formula for
(A) Velocity
(B) Acceleration
(C) Force
(D) Work
Answer:
(C) Force
Question 2.
The error in the measurement of the sides of a rectangle is 1%. The error in the measurement of its area is
(A) 1%
(B) \(\frac{1}{2}\)%
(C) 2%
(D) None of the above.
Answer:
(C) 2%
![]()
Question 3.
Light year is a unit of
(A) Time
(B) Mass
(C) Distance
(D) Luminosity
Answer:
(C) Distance
Question 4.
Dimensions of kinetic energy are the same as that of
(A) Force
(B) Acceleration
(C) Work
(D) Pressure
Answer:
(C) Work
Question 5.
Which of the following is not a fundamental unit?
(A) cm
(B) kg
(C) centigrade
(D) volt
Answer:
(D) volt
2. Answer the following questions.
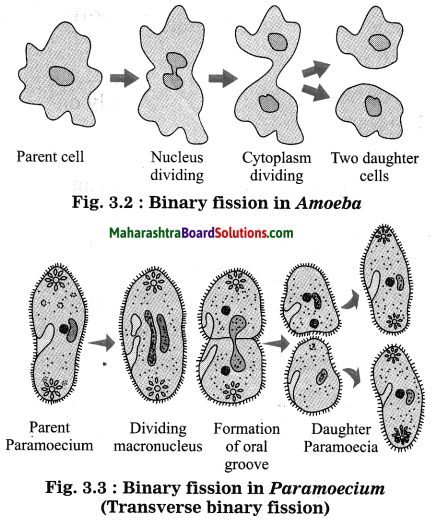
Question 1.
Star A is farther than star B. Which star will have a large parallax angle?
Answer:
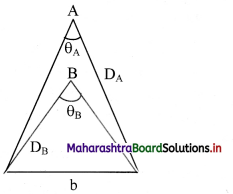
i). ‘b’ is constant for the two stars
∴ θ ∝ \(\frac{1}{D}\)
ii) As star A is farther i.e., DA > DB
⇒ θA < θB
Hence, star B will have larger parallax angle than star A.
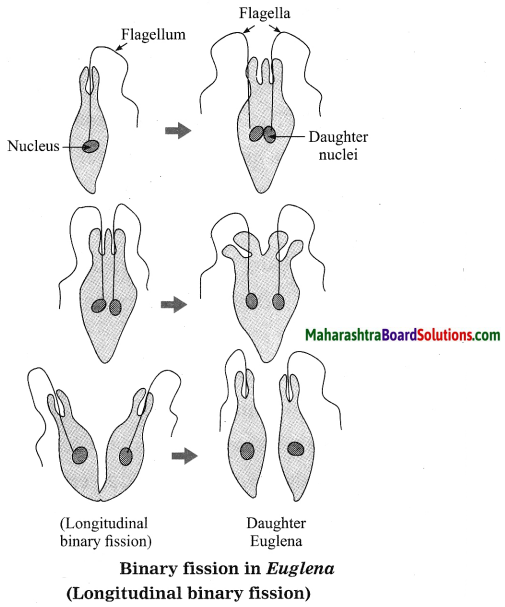
Question 2.
What are the dimensions of the quantity l \(\sqrt{l / g}\), l being the length and g the acceleration due to gravity?
Answer:
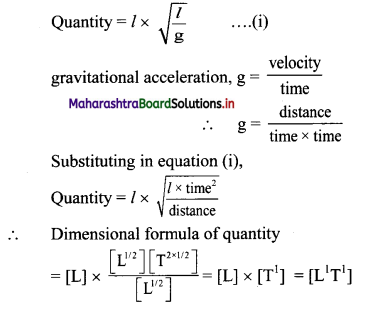
[Note: When power of symbol expressing fundamental quantity appearing in the dimensional formula is not given, ills taken as 1.]
![]()
Question 3.
Define absolute error, mean absolute error, relative error and percentage error.
Answer:
Absolute error:
a. For a given set of measurements of a quantity, the magnitude of the difference between mean value (Most probable value) and each individual value is called absolute error (∆a) in the measurement of that quantity.
b. absolute error = |mean value – measured value|
∆a1 = |amean – a1|
Similarly, ∆a2 = |amean – a2|
. . . ..
. . . .
. . . .
∆an = |amean – an|
Mean absolute error:
For a given set of measurements of a same quantity the arithmetic mean of all the absolute errors is called mean absolute error in the measurement of that physical quantity.
∆amean = \(\frac{\Delta \mathrm{a}_{1}+\Delta \mathrm{a}_{2}+\ldots \ldots .+\Delta \mathrm{a}_{n}}{\mathrm{n}}=\frac{1}{\mathrm{n}} \sum_{\mathrm{i}=1}^{n} \Delta \mathrm{a}_{\mathrm{i}}\)
Relative error:
The ratio of the mean absolute error in the measurement of a physical quantity to its arithmetic mean value is called relative error.
Relative error = \(\frac{\Delta \mathrm{a}_{\mathrm{mean}}}{\mathrm{a}_{\mathrm{mean}}}\)
Percentage error:
The relative error represented by percentage (i.e., multiplied by 100) is called the percentage error.
Percentage error = \(\frac{\Delta \mathrm{a}_{\mathrm{mean}}}{\mathrm{a}_{\mathrm{mean}}}\) × 100%
[Note: Considering conceptual conventions question is modified to define percentage error and not mean percentage error.]
Question 4.
Describe what is meant by significant figures and order of magnitude.
Answer:
Significant figures:
- Significant figures in the measured value of a physical quantity is the sum of reliable digits and the first uncertain digit.
OR
The number of digits in a measurement about which we are certain, plus one additional digit, the first one about which we are not certain is known as significant figures or significant digits. - Larger the number of significant figures obtained in a measurement, greater is the accuracy of the measurement. The reverse is also true.
- If one uses the instrument of smaller least count, the number of significant digits increases.
Rules for determining significant figures:
- All the non-zero digits are significant, for example if the volume of an object is 178.43 cm3, there are five significant digits which are 1,7,8,4 and 3.
- All the zeros between two nonzero digits are significant, eg., m = 165.02 g has 5 significant digits.
- If the number is less than 1, the zero/zeroes on the right of the decimal point and to the left of the first nonzero digit are not significant e.g. in 0.001405, significant. Thus the above number has four significant digits.
- The zeroes on the right hand side of the last nonzero number are significant (but for this, the number must be written with a decimal point), e.g. 1.500 or 0.01500 both have 4 significant figures each.
On the contrary, if a measurement yields length L given as L = 125 m = 12500 cm = 125000 mm, it has only three significant digits.
Order of magnitude:
The magnitude of any physical quantity can be expressed as A × 10n where ‘A’ is a number such that 0.5 ≤ A < 5 then, ‘n’ is an integer called the order of magnitude.
Examples:
- Speed of light in air = 3 × 108 m/s
∴ order of magnitude = 8 - Mass of an electron = 9.1 × 10-31 kg
= 0.91 × 1030 kg
∴ order of magnitude = -30
![]()
Question 5.
If the measured values of two quantities are A ± ∆A and B ± ∆B, ∆A and ∆B being the mean absolute errors. What is the maximum possible error in A ± B? Show that if Z = \(\frac{A}{B}\)
\(\frac{\Delta Z}{Z}=\frac{\Delta A}{A}+\frac{\Delta B}{B}\)
Answer:
Maximum possible error in (A ± B) is (∆A + ∆B).
Errors in divisions:
i) A
Suppose, Z = \(\frac{A}{B}\) and measured values of A and B are (A ± ∆A) and (B ± ∆B) then,
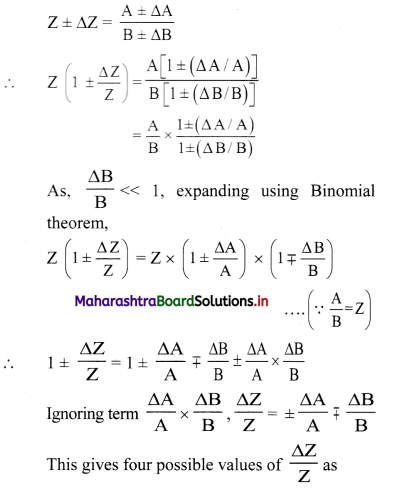
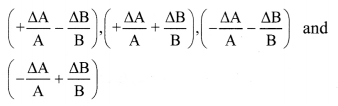
∴ Maximum relative error of \(\frac{\Delta Z}{Z}=\pm\left(\frac{\Delta \mathrm{A}}{\mathrm{A}}+\frac{\Delta \mathrm{B}}{\mathrm{B}}\right)\)
ii) Thus, when two quantities are divided, the maximum relative error in the result is the sum of relative errors in each quantity.
Question 6.
Derive the formula for kinetic energy of a particle having mass m and velocity v using dimensional analysis
Answer:
Kinetic energy of a body depends upon mass (m) and velocity (v) of the body.
Let K.E. ∝ mx vy
∴ K.E. = kmx vy …….. (1)
where,
k = dimensionless constant of proportionality. Taking dimensions on both sides of equation (1),
[L2M1T-2] – [L0M1T0]x [L1M0T-1]y
= [L0MxT0] [LyM0T-y]
= [L0+yMx+0T0-y]
[L2M1T2] = [LyMxT-y] …………. (2)
Equating dimensions of L, M, T on both sides of equation (2),
x = 1 and y = 2 ,
Substituting x, y in equation (1), we have
K.E. = kmv2
3. Solve numerical examples.
Question 1.
The masses of two bodies are measured to be 15.7 ± 0.2 kg and 27.3 ± 0.3 kg. What is the total mass of the two and the error in it?
Answer:
Given: A ± ∆A = 15.7 ± 0.2kg and
B ± ∆B = 27.3 ± 0.3 kg.
To find: Total mass (Z), and total error (∆Z)
Formulae: i. Z = A + B
ii) ±∆Z = ±∆A ± ∆B
Calculation: From formula (i),
Z = 15.7 + 27.3 = 43 kg
From formula (ii),
± ∆Z (± 0.2) + (± 0.3)
=±(0.2 + 0.3)
= ± 0.5 kg
Total mass is 43 kg and total error is ± 0.5 kg.
Question 2.
The distance travelled by an object in time (100 ± 1) s is (5.2 ± 0.1) m. What is the speed and it’s relative error?
Answer:
Given: Distance (D ± ∆D) = (5.2 ± 0.1) m,
time(t ± ∆t) = (100 ± 1)s.
To find: Speed (v), maximum relative error \(\left(\frac{\Delta \mathrm{v}}{\mathrm{v}}\right)\)
Formulae: i. v = \(\frac{\mathrm{D}}{\mathrm{t}}\)
ii. \(\frac{\Delta \mathrm{v}}{\mathrm{v}}=\pm\left(\frac{\Delta \mathrm{D}}{\mathrm{D}}+\frac{\Delta \mathrm{t}}{\mathrm{t}}\right)\)
Calculation: From formula (i),
v = \(\frac{5.2}{100}\) = 0.052 m/s
From formula (ii),
\(\frac{\Delta \mathrm{v}}{\mathrm{v}}=\pm\left(\frac{0.1}{5.2}+\frac{1}{100}\right)\)
= \(\pm\left(\frac{1}{52}+\frac{1}{100}\right)=\pm \frac{19}{650}\)
= ± 0.029 rn/s
The speed is 0.052 m/s and its maximum relative error is ± 0.029 m/s.
[Note: Framing of numerical is modified to make it specific and meaningful.]
![]()
Question 3.
An electron with charge e enters a uniform. magnetic field \(\vec{B}\) with a velocity \(\vec{v}\). The velocity is perpendicular to the magnetic field. The force on the charge e is given by
|\(\vec{F}\)| = Bev Obtain the dimensions of \(\vec{B}\).
Answer:
Given: |\(\vec{F}\)| = B e v
Considering only magnitude, given equation is simplified to,
F = B e v

∴ B = [L0M1T-2I-1]
[Note: The answer given above is calculated in accordance with textual method considering the given data.]
Question 4.
A large ball 2 m in radius is made up of a rope of square cross section with edge length 4 mm. Neglecting the air gaps in the ball, what is the total length of the rope to the nearest order of magnitude?
Answer:
Volume of ball = Volume enclosed by rope.
\(\frac{4}{3}\) π (radius)3 = Area of cross-section of rope × length of rope.
∴ length of rope l = \(\frac{\frac{4}{3} \pi r^{3}}{A}\)
Given:
r = 2 m and
Area = A = 4 × 4 = 16 mm2
= 16 × 10-6 m2
∴ l = \(\frac{4 \times 3.142 \times 2^{3}}{3 \times 16 \times 10^{-6}}\)
= \(\frac{3.142 \times 2}{3}\) × 10-6 m
≈ 2 × 106 m.
Total length of rope to the nearest order of magnitude = 106 m = 103 km
Question 5.
Nuclear radius R has a dependence on the mass number (A) as R = 1.3 × 10-16 A\(\frac{1}{3}\) m. For a nucleus of mass number A=125, obtain the order of magnitude of R expressed in metre.
Answer:
R= 1.3 × 10-16 × A\(\frac{1}{3}\) m
For A = 125
R= 1.3 × 10-16 × (125)\(\frac{1}{3}\)
= 1.3 × 10-16 × 5
= 6.5 × 10-16
= 0.65 × 10-15 m
∴ Order of magnitude = -15
[Note: Taking the standard value of nuclear radius R = 1.3 × 10-155 m, the order of magnitude comes to be 10-14 m.]
Question 6.
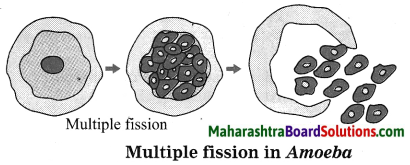
In a workshop a worker measures the length of a steel plate with a Vernier callipers having a least count 0.01 cm. Four such measurements of the length yielded the following values: 3.11 cm, 3.13 cm, 3.14 cm, 3.14 cm. Find the mean length, the mean absolute error and the percentage error in the measured value of the length.
Answer:
Given: a1 = 3.11 cm, a2 = 3.13 cm,
a3 = 3.14 cm. a4 = 3.14cm
Least count L.C. = 0.01 cm.
To find.
i. Mean length (amean)
ii. Mean absolute error (∆amean)
iii. Percentage error.
Formulae: i. amean = \(\frac{a_{1}+a_{2}+a_{3}+a_{4}}{4}\)
ii. ∆an = |amean – an|
iii. ∆amean = \(\frac{\Delta \mathrm{a}_{1}+\Delta \mathrm{a}_{2}+\Delta \mathrm{a}_{3}+\Delta \mathrm{a}_{4}}{4}\)
iv. Percentage error = \(\frac{\Delta \mathrm{a}_{\mathrm{mean}}}{\mathrm{a}_{\text {mean }}}\) × 100
Calculation: From formula (i),
amean = \(\frac{3.11+3.13+3.14+3.14}{4}\)
= 3.13 cm
From formula (ii),
∆a1 = |3.13 – 3.11| = 0.02 cm
∆a2 = |3.13 – 3.13| = 0
∆a3 = |3.13 – 3.14| = 0.01 cm
∆a4 = |3.13 – 3.14| = 0.01 cm
From formula (iii),
∆amean = \(\frac{0.02+0+0.01+0.01}{4}\) = 0.01 cm
From formula (iii).
% error = \(\frac{0.01}{3.13}\) × 100
= \(\frac{1}{3.13}\)
= 0.3196
……..(using reciprocal table)
= 0.32%
i. Mean length is 3.13 cm.
ii. Mean absolute error is 0.01 cm.
iii. Percentage error is 0.32 %.
[Note: As per given data of numerical, percentage error calculation upon rounding off yields percentage error as 0.32%]
![]()
Question 7.
Find the percentage error in kinetic energy of a body having mass 60.0 ± 0.3 g moving with a velocity 25.0 ± 0.1 cm/s.
Answer:
Given: m = 60.0 g, v = 25.0 cm/s.
∆m = 0.3 g, ∆v = 0.1 cm/s
To find: Percentage error in E
Formula: Percentage error in E
\(\left(\frac{\Delta \mathrm{m}}{\mathrm{m}}+2 \frac{\Delta \mathrm{v}}{\mathrm{v}}\right)\) × 100%
Calculation: From formula,
Percentage error in E
= \(\left(\frac{0.3}{60.0}+2 \times \frac{0.1}{25.0}\right)\) × 100%
= 1.3%
The percentage error in energy is 1.3%.
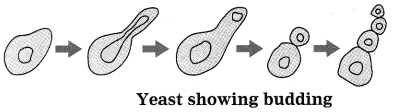
Question 8.
In Ohm’s experiments, the values of the unknown resistances were found to be 6.12 Ω , 6.09 Ω, 6.22 Ω, 6.15 Ω. Calculate the mean absolute error, relative error and percentage error in these measurements.
Answer:
Given: a1 = 6.12 Ω, a2 = 6.09 Ω, a3 = 6.22 Ω, a4 = 6.15 Ω,
To find:
i) Absolute error (∆amean)
ii) Relative error
iii) Percentage error
Formulae:
i) amean = \(\frac{a_{1}+a_{2}+a_{3}+a_{4}}{4}\)
ii) ∆an = |amean – an|
iii) ∆amean = \(\frac{\Delta \mathrm{a}_{1}+\Delta \mathrm{a}_{2}+\Delta \mathrm{a}_{3}+\Delta \mathrm{a}_{4}}{4}\)
iv) Percentage error = \(\frac{\Delta \mathrm{a}_{\mathrm{mean}}}{\mathrm{a}_{\text {mean }}}\) × 100
From formula (ii),
∆a1 = |6.145 – 6.12|= 0.025
∆a2 = |6.145 – 6.09| = 0.055
∆a3 = |6.145 – 6.22| = 0.075
∆a4 = |6.l45 – 6.15| = 0.005
From formula (iii),
∆amean = \(\frac{0.025+0.055+0.075+0.005}{4}=\frac{0.160}{4}\)
= 0.04 Ω
From formula (iv),
Relative error = \(\frac{0.04}{6.145}\) = 0.0065 Ω
From formula (v).
Percentage error = 0.0065 \frac{0.04}{6.145} 100 = 0.65%
i. The mean absolute error is 0.04 Ω.
ii. The relative error is 0.0065 Ω.
iii. The percentage error is 0.65%.
[Note: Framing of numerical is modified to reach the answer given to the numerical.]
Question 9.
An object is falling freely under the gravitational force. Its velocity after travelling a distance h is v. If v depends upon gravitational acceleration g and distance, prove with dimensional analysis that v = k\(\sqrt{g h}\) where k is a constant.
Answer:
Given = v = k\(\sqrt{g h}\)
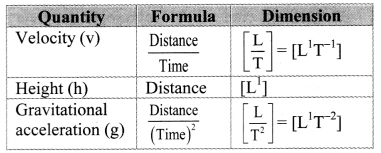
k being constant is assumed to be dimensionless.
Dimensions of L.H.S. = [v] = [L1T-1]
Dimension of R.H.S. = [latex]\sqrt{g h}[/latex]
= [L1T-2]\(\frac{1}{2}\) × [L1]\(\frac{1}{2}\)
= [L2T-2]\(\frac{1}{2}\)
= [L1T-1]
As, [L.H.S.] = [R.H.S.],
=> v = k\(\sqrt{g h}\)is dimensionally correct equation.
Question 10.
v = at + \(\frac{b}{t+c}\) + v0 is a dimensionally valid equation. Obtain the dimensional formula for a, b and c where v is velocity, t is time and v0 is initial velocity.
Answer:
Solution: Given: y = at + \(\frac{b}{t+c}\) + + v0
As only dimensionally identical quantities can be added together or subtracted from each other, each term on R.H.S. has dimensions of L.H.S. i.e., dimensions of velocity.
∴ [LH.S.] = [v] = [L1T-1]
This means, [at] = [v] = [L1T-1]
Given, t = time has dimension [T-1]
∴ [a] = \(\frac{\left[\mathrm{L}^{1} \mathrm{~T}^{-1}\right]}{[\mathrm{t}]}=\frac{\left[\mathrm{L}^{1} \mathrm{~T}^{-1}\right]}{\left[\mathrm{T}^{1}\right]}\) = [L1T-2] = L1M0T-2]
Similarly, [c] = [t] = [T1] = [L0M0T1]
∴ \(\frac{[\mathrm{b}]}{\left[\mathrm{T}^{1}\right]}\) = [v] = [L1T-1]
∴ [b] = [L1T-1] × [T1] = [L1] = [L1M0T0]
![]()
Question 11.
The length, breadth and thickness of a rectangular sheet of metal are 4.234 m, 1.005 m, and 2.01 cm respectively. Give the area and volume of the sheet to correct significant figures.
Answer:
Given: l = 4.234 m, b = 1.005 m,
t = 2.01 cm = 2.01 × 10-2 m = 0.0201 m
To find:
i) Area of sheet to correct significant figures (A)
ii) Volume of sheet to correct significant figures (V)
Formulae: i. A = 2(lb + bt + tl)
iii) V = l × b × t
Calculation: From formula (i),
A = 2(4.234 × 1.005 + 1.005 × 0.0201 +0.0201 × 4.234)
= 2 |[antilog(log 4.234 + logl .005) + antiiog(log 1.005 + log0.0201) + antilog(log 0.0201 + log 4.234)]}
= 2{[antilog(0.6267 + 0.0021) + antilog(0.0021 + \(\overline{2}\) .3010) + antilog (\(\overline{2}\) .3010 + 0.6267)]}
= 2 {[antilog(0.6288) + antilog (\(\overline{2}[/latex .3031) +antilog([latex]\overline{2}\) .9277)]}
= 2 [4.254 + 0.02009 + 0.08467]
= 2 [4.35876]
= 8.71752m2
In correct significant figure,
A = 8.72 m2 From formula (ii),
V =4.234 × 1.005 × 0.0201
= antilog [log (4.234) + log (1.005) + log (0.0201)]
= antilog [0.6269 – 0.0021 – \(\overline{2}\).3032]
= antilog [0.6288 – \(\overline{2}\).3032]
= antilog [ 2 .9320]
= 8.551 × 10-2
= 0.08551 m3
In correct significant figure (rounding off),
V = 0.086 m3
i.) Area of sheet to correct significant figures is 8.72 m2.
ii) Volume of sheet to correct significant figures is 0.086 m3.
[Note: The given solution is arrived to by considering a rectangular sheet.]
Question 12.
If the length of a cylinder is l = (4.00 ± 0.001) cm, radius r = (0.0250 ± 0.001) cm and mass m = (6.25 ± 0.01) gm. Calculate the percentage error in the determination of density.
Answer:
Given: l = (4.00 ± 0.001) cm,
In order to have same precision, we use, (4.000 ± 0.001),
r = (0.0250 ± 0.00 1) cm,
In order to have same precision, we use, (0.025 ± 0.001)
m = (6.25 ± 0.01) g
To find: percentage error in density
Formulae:
i) Relative error in volume, \(\frac{\Delta \mathrm{V}}{\mathrm{V}}=\frac{2 \Delta \mathrm{r}}{\mathrm{r}}+\frac{\Delta l}{l}\)
….(∵ Volume of cylinder, V = πr2l)
ii) Releative error \(\frac{\Delta \rho}{\rho}=\frac{\Delta m}{m}+\frac{\Delta V}{V}\)
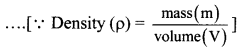
iii) Percentage error= Relative error × 100%
Calculation.
From formulae (i) and (ii),
∴ \(\frac{\Delta \rho}{\rho}=\frac{\Delta \mathrm{m}}{\mathrm{m}}+\frac{2 \Delta \mathrm{r}}{\mathrm{r}}+\frac{\Delta l}{l}\)
= \(\frac{0.01}{6.25}+\frac{2(0.001)}{0.025}+\frac{0.001}{4.000}\)
= 0.00 16 + 0.08 + 0.00025
= 0.08 185
From formula (iii).
% error in density = \(\frac{\Delta \rho}{\rho}\) × 100
= 0.08185 × 100
= 8.185%
Percentage error in density is 8.185%.
![]()
Question 13.
When the planet Jupiter is at a distance of 824.7 million kilometers from the Earth, its angular diameter is measured to be 35.72″ of arc. Calculate the diameter of the Jupiter.
Answer:
Given: Angular diameter (a) = 35.72″
= 35.72″ × 4.847 × 10-6 rad
1.73 × 10-4 rad
Distance from Earth (D)
= 824.7 million km
= 824.7 × 106 km
= 824.7 × 109 m.
To find: Diameter of Jupiter (d)
Formula: d = α D
Calculation: From formula,
d = 1.73 × 10-4 × 824.7 × 109
= 1.428 × 108 m
= 1.428 × 105 km
Diameter of Jupiter is 1.428 × 105 km.
Question 14.
If the formula for a physical quantity is X = \(\frac{a^{4} b^{3}}{c^{1 / 3} d^{1 / 2}}\) and if the percentage error in the measurements of a, b, c and d are 2%, 3%, 3% and 4% respectively. Calculate percentage error in X.
Answer:
Given X = \(\frac{a^{4} b^{3}}{c^{1 / 3} d^{1 / 2}}\)
Percentage error in a, b, c, d is respectively 2%, 3%, 3% and 4%.
Now, Percentage error in X
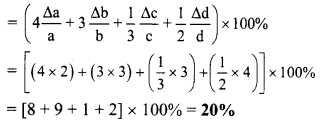
Question 15.
Write down the number of significant figures in the following: 0.003 m2, 0.1250 gm cm-2, 6.4 × 106 m, 1.6 × 10-19 C, 9.1 × 10-31 kg.
Answer:
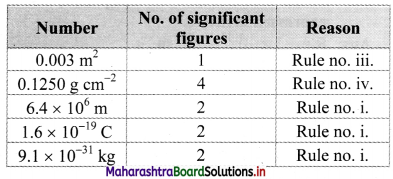
Question 16.
The diameter of a sphere is 2.14 cm. Calculate the volume of the sphere to the correct number of significant figures.
Answer:
Volume of sphere = \(\frac{4}{3}\) πr3
= \(\frac{4}{3}\) × 3.142 × (\(\frac{2.14}{2}\))3 ………….. (∵ r = \(\frac{d}{2}\))
= \(\frac{4}{3}\) × 3.142 × (1.07)3
= 1.333 × 3.142 × (1.07)3
= {antilog [log (1.333) + log(3.142)+3 log(1.07)]}
= {antilog [0.1249 + 0.4972 + 3 (0.0294)])
= {antilog [0.6221 + 0.0882]}
= {antilog [0.7103]}
= 5.133cm3
In multiplication or division, the final result should retain as many significant figures as there are in the original number with the least significant figures.
Volume in correct significant figures
∴ 5.13 cm3
11th Physics Digest Chapter 1 Units and Measurements Intext Questions and Answers
Can you recall (Textbook Page No. 1)
Question 1.
i) What is a unit?
ii) Which units have you used in the laboratory for measuring
a. length
b. mass
c. time
d. temperature?
iii. Which system of units have you used?
Answer:
- The standard measure of any quantity is called the unit of that quantity.
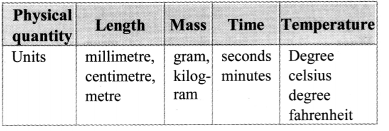
- MKS or SI system is used mostly. At times. even CGS system is used.
Can you tell? (Textbook Page No. 8)
Question 1.
If ten students are asked to measure the length of a piece of cloth upto a mm, using a metre scale, do you think their answers will be identical? Give reasons.
Answer:
Answers of the students are likely to be different. Length of cloth needs to be measured up to a millimetre (mm) length. Hence, to obtain accurate and precise reading one must use measuring instrument having least count smaller than 1 mm.
But least count of metre scale is 1 mm. As a result, even smallest uncertainty in reading would vary reading significantly. Also, skill of students doing measurement may also introduce uncertainty in observation.
Hence, their answers are likely to be different.
Activity (Textbook Page No. 10)
Perform an experiment using a Vernier callipers of least count 0.01cm to measure the external diameter of a hollow cylinder. Take 3 readings at different positions on the cylinder and find (i) the mean diameter (ii) the absolute mean error and (iii) the percentage error in the measurement of diameter.
Answer:
Given: L.C. = 0.01 cm
To measure external diameter of hollow cylinder readings are taken as follows:
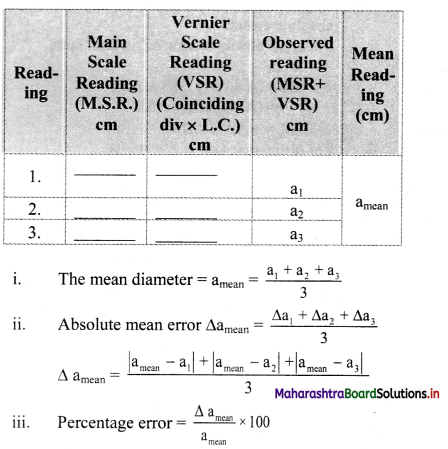
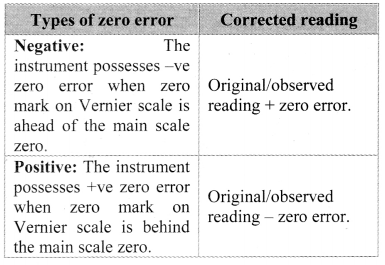
[Note: The above table is made assuming zero error in Vernier calipers. If caliper has positive or negative zero error, the zero error correction needs to be introduced into observed reading.]
Internet my friend (Textbook Page No. 12)
i. ideoiectures.net/mit801f99_lewin_lec0l/
ii. hyperphysicsphy-astr.gsu.ed u/libase/hfra me. html
[Students can use links given above as a reference and collect information about units and measurements]
Maharashtra State Board Class 11 Physics Textbook Solutions
- Units and Measurements Class 11 Physics Textbook Solutions
- Mathematical Methods Class 11 Physics Textbook Solutions
- Motion in a Plane Class 11 Physics Textbook Solutions
- Laws of Motion Class 11 Physics Textbook Solutions
- Gravitation Class 11 Physics Textbook Solutions
- Mechanical Properties of Solids Class 11 Physics Textbook Solutions
- Thermal Properties of Matter Class 11 Physics Textbook Solutions
- Sound Class 11 Physics Textbook Solutions
- Optics Class 11 Physics Textbook Solutions
- Electrostatics Class 11 Physics Textbook Solutions
- Electric Current Through Conductors Class 11 Physics Textbook Solutions
- Magnetism Class 11 Physics Textbook Solutions
- Electromagnetic Waves and Communication System Class 11 Physics Textbook Solutions
- Semiconductors Class 11 Physics Textbook Solutions