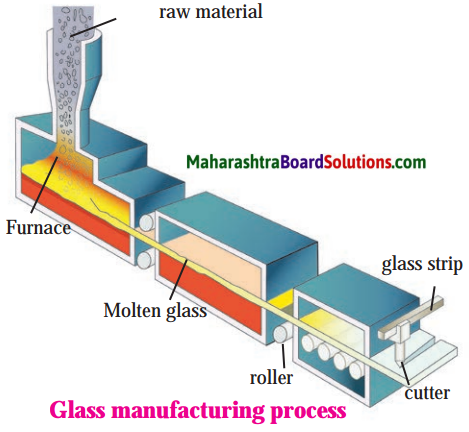
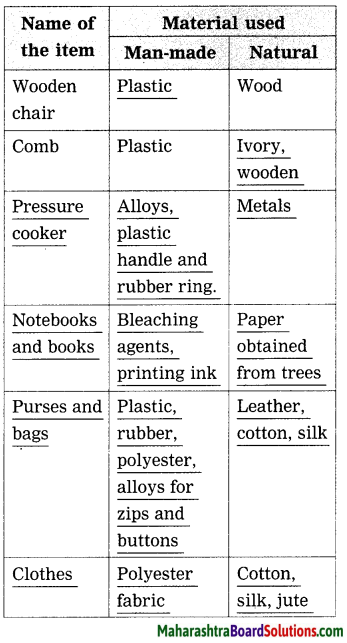
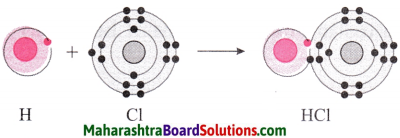
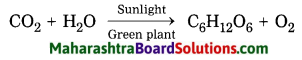
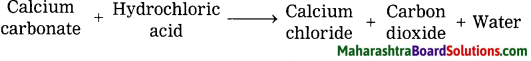
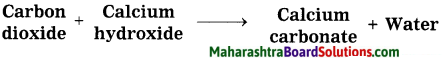
Std 8 Science Chapter 8 Pollution Question Answer Maharashtra Board
Balbharti Maharashtra State Board Class 8 Science Solutions Chapter 8 Pollution Notes, Textbook Exercise Important Questions and Answers.
Class 8 Science Chapter 8 Pollution Question Answer Maharashtra Board
Class 8 Science Chapter 8 Pollution Textbook Questions and Answers
1. Following are some statements about pollution. Which type of pollution do those express:
Question a.
Fog seems to be appearing in Delhi during day hours.
Answer:
Air pollution-Smog
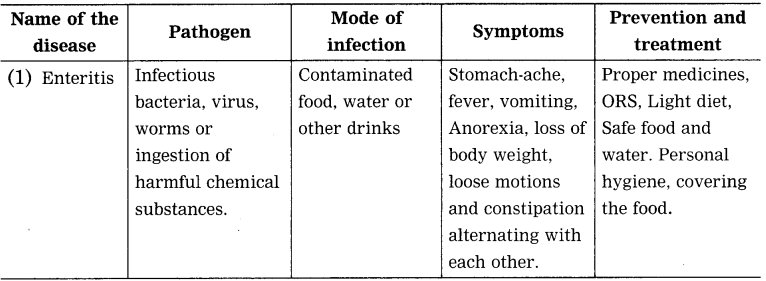
(The sentence should have the word Smog and not fog. Smog is fog with smoke. Only fog cannot be polluting, but the smog is.)
Question b.
Many times, vomiting and dysentery occurs after eating ‘panpuri’.
Answer:
Water pollution-Contaminated food and water due to bacteria or virus
Question c.
Problem of sneezing occurs sometimes during visit to garden.
Answer:
Air pollution due to pollens
Question d.
Crop does not grow up in some areas.
Answer:
Soil pollution
Question e.
People living in the busy squares face the problems like short breathing and other respiratory problems.
Answer:
Air pollution due to traffic
![]()
2. Read the passage and identify the sentences expressing types of pollution.
Question a.
Nilesh is a student of Std. VII and lives in urban area. It takes about an hour to go to the school by bus. He faces the heavy traffic of two wheelers, four wheelers, rickshaws, buses while going to school. He is facing the problem of asthma since last few days, Doctors recommended him to stay away from urban area. Since then, his mother sent him to the village of his maternal uncle, Nilesh saw the heaps of garbage at many places in village. Foul smell of human and animal wastes was present at many places. Blackish water with foul smell was flowing in a stream. He developed some abdominal disease within few days.
Answer:
- It takes about an hour to go to the school. (Due to traffic jam, Nilesh is spending more time in polluted, contaminated air.)
- He faces the heavy traffic. (Large scale combustion of fossil fuel.)
- He is facing the problem of asthma. (Air pollution – Harmful to human health.)
- The heaps of garbage at many places. (Solid waste – Land pollution.)
- Foul smell of human and animal wastes. (Biological pollution, air pollution.)
- Blackish water with foul smell was flowing in a stream. (Improper sewage management – Water pollution.)
- He developed some abdominal disease within few days. (Water pollution – Effect on human health.)
3. Match the pairs from ‘A’ and ‘B’ columns and explain the effect of pollution on human health.
Question a.
| Column ‘A’ | Column ‘B’ |
| 1. Water containing cobalt | a. Mental retardation |
| 2. Methane gas | b. Paralysis |
| 3. Water containing lead | c. Inflammation of lungs |
| 4. Sulphur dioxide | d. Skin cancer |
| 5. Nitrogen dioxide | e. Irritation of eyes |
Answer:
| Column ‘A’ | Column ‘B’ |
| 1. Water containing cobalt | b. Paralysis |
| 2. Methane gas | d. Skin cancer |
| 3. Water containing lead | a. Mental retardation |
| 4. Sulphur dioxide | e. Irritation of eyes |
| 5. Nitrogen dioxide | c. Inflammation of lungs |
![]()
4. True or false.
Question a.
Water does not get polluted by washing the clothes in running water of river.
Answer:
False. (Even if washing of soiled clothes is done in running water, it will cause pollution as the dirt and the waste materials will be added to water. This certainly will cause water pollution.)
Question b.
More the use of electric appliances, more will be the pollution.
Answer:
True. (Most of the electricity is generated in India by burning coal. The power generation plants thus cause lots of air pollution. More the electricity is used by using more appliances, there will be more pollution. However, only power generation through solar energy cannot cause pollution.)
5. Answer the following:
Question a.
What is pollution?
Answer:
Contamination of natural environment that can harmfully affect the environment is called pollution.
Question b.
What are Pollutants?
Answer:
The products which affect the normal functioning of ecosystem and have an adverse effect on plants, animals and humans are called pollutants.
Question c.
What is acid rain?
Answer:
1. When rainwater contains harmful amounts of nitric and sulphuric acids, it is called acid rain.
2. Burning of fossil fuels such as coal, wood, petroleum, etc. releases nitrogen oxide and sulphur oxide into the atmospheric air.
3. Since these oxides are soluble in water, they dissolve in rainwater. Nitrogen and sulphur oxides dissolved in large quantities of water vapour form acids like nitric acid, nitrous acid, sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid.
4. These acids mix with mist, drops of rainwater and snow. They change their composition and fall back on the ground in the form of acid rain.
5. Effects of acid rain are as follows:
- Increase in the acidity of soil and water bodies.
- Damage to the trees.
- Water becomes unsuitable for fish and wildlife.
- Buildings, statues, sculptures, bridges, monuments and fences are corroded due to acid rain. Thus, acid rain damages our national assets.
- Acid rain affects agriculture and crop lands.
![]()
Question d.
What is greenhouse effect?
Answer:
- Greenhouse effect is the ; phenomenon due to which global warming and climate change occur.
- The earth receives solar energy in the form of heat from the sun. The surface of earth absorbs this heat and reflects it back to the atmosphere as infrared radiation. Some of this heat energy goes directly into space.
Question e.
Which are visible pollutants known to you?
Answer:
1. The polluting substances that are seen easily with the naked eyes can be called as visible pollutants. E.g. Solid wastes, plastic articles, plastic bags, the suspended things in the water, metal refuse, etc.
Question f.
Which are invisible pollutants?
Answer:
The pollutants which are completely dissolved in water or mixed in the air, cannot be seen and hence they can be called invisible pollutants. Since they are not seen, we remain unaware about the presence of these pollutants. E.g. the insecticides spread f on the crops. Aerosols, many hazardous gases in the air, toxic compounds that are totally soluble in water, etc.
6. Answer the following.
Question a.
Give two examples of each of water, soil and air pollution from your residential area.
Answer:
Air pollution:
- New buildings are constructed. Old structures are demolished. This is creating lots of dust pollution. The air is full of particulate matter.
- The number of vehicles on the road has tremendously increased. This causes smoky environment.
Water pollution:
- The sea shows lots of floating plastic and decaying flowers, etc. When beaches are visited it is a common sight.
- Many fishes are seen dying in great numbers and are washed off to the shore.
Soil pollution :
- Everywhere garbage heaps are seen. In that plastic bags, needles, old medicine vials and cartons are seen in abundance.
- The sludge brought by rainwater is spread everywhere and that causes stink.
![]()
Question b.
How does the pollution occur due to vehicles? Give the names of vehicles causing least pollution.
Answer:
- More than 50% of the air pollution is caused by vehicular traffic.
- Particulate matter, unburnt hydrocarbons, CO, nitrogen oxides and carcinogenic hydrocarbons are present in the automobile exhausts.
- Fossil fuels like petrol, diesel, natural gas, gasoline, etc. which are burnt to run the automobiles lead to the emission of CO2 and other gases.
- Therefore, vehicles are said to be the major contributors to air pollution.
- The only vehicle which is non¬polluting is bicycle. The four-wheelers which are battery operated are also manufactured recently.
These two types of vehicles are eco-friendly. The cars that run on C.N.G. are also said to be lesser polluting.
Question c.
What are natural reasons causes for water pollution?
Answer:
The natural causes of the water pollution:
1. If organic pollutants are added to the water there is an overgrowth of weeds such as Eichhornia. The growth of algae also makes the water unsuitable for consumption. These aquatic plants release oxygen during daytime but by night they require oxygen thus depleting the dissolved oxygen level. The natural characters of water are then changed.
2. The decomposing matter when added to the water make it polluted and stinking.
3. Due to deposition of sludge or eroded soil, the rivers change their path and divert from original flow. The currents are also changed. Deposition of sludge makes the water polluted.
4. Due to soil erosion, surrounding the water bodies, the microbes, bacteria, protozoans and the worms and larvae of nematodes enter the water causing severe biological pollution. Many inorganic pollutants are also added to the water. The fungand bacteria present in the water make it non-potable. Such water spreads water-borne diseases.
![]()
Question d.
Suggest four preventive measures for air pollution.
Answer:
The following methods are adopted to control air pollution from the industries:
- The source discharge is diluted by tall chimneys.
- There are source correction methods like changing the raw material, equipment modification, process modification, etc.
- Effective pollution controlling equipment like dust collectors, electrostatic precipitators, wet scrubbers, etc. should be used.
- There should be ban and control over atomic tests and chemical weapons on the international level.
Question e.
Explain relation between greenhouse effect and global warming.
Answer:
Because of greenhouse effect, there is increase in the global temperature. The heat on the earth remains trapped due to envelope of greenhouse gases. The percentage of carbon dioxide and methane is constantly increasing and hence there is increase in the temperature too. Thus the greenhouse effect is directly related to the global warming.
Effects of this relation between greenhouse effect and global warming are as follows:
- The polar ice caps and the glaciers at both the poles are melting due to increased temperature.
- The oceans’ water is rising due to this melted ice. The sea level rise is causing coastal land submergence. The islands at various regions are threatened of drowning.
- Many species of living organisms are already extinct due to global warming. The rest are also threatened.
- Wild animals are showing weird migrations. Polar bear is endangered.
- The increased temperature of the oceanic water is causing many changes in the tides and currents. This results into increased occurrence of cyclones, hurricanes and cloud bursting. The natural disasters are rising in last decade.
- The agricultural production is decreasing. The regions with less rainfall are facing draughts.
![]()
Question f.
Construct two slogans each on air, water and soil pollution.
Answer:
Air pollution:
- Be a part of the solution and not part of pollution.
- Show your care, clean your air.
Water pollution:
- Water, water everywhere, Not a drop to drink. The pollution is making all the water stink.
- Save the fish and the little turtle. Don’t throw plastic or it will encircle.
Soil Pollution:
- Don’t be mean, keep environment clean.
- Let’s keep land clean, together only we can win.
7. Classify the following pollutants into natural and manmade categories.
Question
Classify the following pollutants into natural and manmade categories.
Sewage, dust, pollen grains, chemical fertilizers, vehicular smoke, algae, pesticides, waste of animals and birds.
Answer:
| Man-made | Natural |
| 1. Sewage | 1. Dust (Natural) |
| 2. Dust (Construction related) | 2. Pollen grains |
| 3. Chemical fertilizers | 3. Algae |
| 4. Vehicular smoke | 4. Waste (Excreta) of animals and |
| 5. Pesticides |
![]()
Project:
Question 1.
Visit the water testing laboratory in your area and collect the information about tests for checking the purity of water.
Question 2.
Visit the square having heavy traffic in your area and report the pollution at different times of day and find out the duration of maximum pollution.
Class 8 Science Chapter 8 Pollution Additional Important Questions and Answers
Rewrite the sentences after filling the blanks:
Question 1.
Natural pollutants are destroyed in due course of time by …………. .
Answer:
Natural pollutants are destroyed in due course of time by nature’s rule.
Question 2.
Air pollutants with ……….. cause colour change in paints, oil paintings, nylon, etc.
Answer:
Air pollutants with sulphur cause colour change in paints, oil paintings, nylon, etc.
![]()
Question 3.
Boards indicating the …………. are displayed in busy squares in metro cities.
Answer:
Boards indicating the air quality index are displayed in busy squares in metro cities.
Question 4.
Soil ………… decreases due to pollution.
Answer:
Soil fertility decreases due to pollution.
Question 5.
Problem of …………… pollution increases due to soil pollution.
Answer:
Problem of water pollution increases due to soil pollution.
State whether the following statements are True or False. Explain your statement:
Question 1.
Polluted water is responsible for diseases such as cholera, hepatitis, typhoid, skin diseases and diseases of the alimentary canal.
Answer:
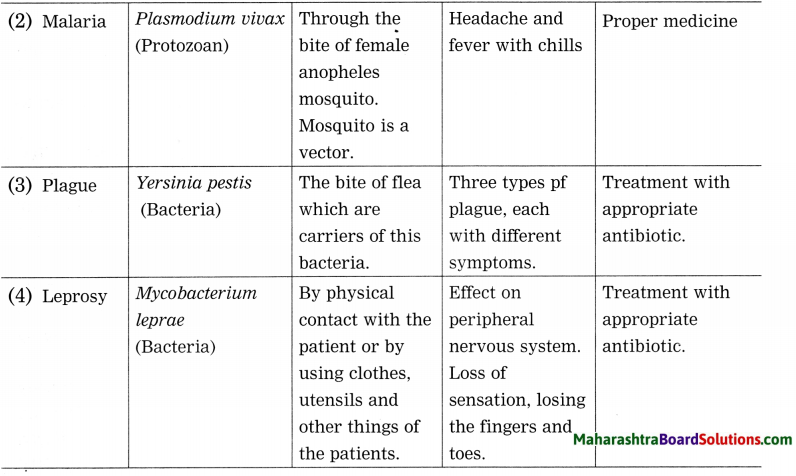
True. (The water sources if they are contaminated with biological pollutants such as bacteria, viruses or protozoans, can cause variety of water-borne diseases.)
![]()
Question 2.
When water is mixed with natural or artificial unwanted material, the dissolved oxygen level of such water increases.
Answer:
False. (When water is mixed with natural or artificial unwanted material, the dissolved oxygen level of such water decreases. This causes harm to the resident animals. However when aquatic weeds and algae outgrow in number it causes rise in oxygen only during day time.)
Question 3.
Though any amount of pollutants are added to the soil, the toxic substances do not leach into water.
Answer:
False. (The toxic substances added to the soil can leach in the groundwater and cause water pollution.)
Identify the odd term:
Question 1.
Industrialization, Population explosion, Mining, Vehicular transport, Dust storms.
Answer:
Dust storms (All others are man-made causes environmental degradation.)
Question 2.
Poisoning, asthma, Silicosis, respiratory diseases.
Answer:
Silicosis (All others are effects of methane.)
Question 3.
Irritation of eyes, respiratory tract, excess mucus, mental weakness
Answer:
Mental weakness (All other are effects of sulphur dioxide.)
![]()
Question 4.
Volcanic eruption, Earthquake, Atomic explosion, Forest fires.
Answer:
Atomic explosion (All others are natural causes of air pollution.)
Question 5.
Uranium, Sulphur, Thorium, Plutonium.
Answer:
Sulphur (All others are elements which are used in the production of atomic energy.)
Consider the relation between the items in the first pair and write the correlation for second pair:
Question 1.
Industrialization: Sulphur compounds : :…………………. : Lead compounds
Answer:
Use of fuels/Transportation
Question 2.
City where smoke and soot caused it to be called black city : Petersburg : : Indian city where worst ever industrial accident has occurred : ……………….
Answer:
Bhopal
Question 3.
Arsenic and Cadmium : Inorganic water pollutants : : Weedicides and insecticides : ………….
Answer:
Organic water pollutants.
Write definitions:
Question 1.
Air pollution.
Answer:
Contamination of air by toxic gaseous and particulate pollutants in concentration which is harmful to human beings and his surroundings is called air pollution.
![]()
Question 2.
Water pollution.
Answer:
When toxic and unwanted substances enter, dissolve or remain suspended in the water bodies deteriorating the quality of water and affecting the aquatic ecosystem, then it is known as water pollution.
Question 3.
Soil pollution.
Answer:
Soil pollution is the phenomenon caused due to natural or man-made causes, which occurs when there are changes in its physical, biological and chemical properties of the soil leading to decreased fertility due to either natural or man-made reasons.
Distinguish between the following:
Question 1.
Degradable and Non-degradable pollutants:
| Degradable pollutants | Non-degradable pollutants |
| 1. Degradable pollutants can degrade on their own after some time. | 1. non-degradable pollutants cannot degrade on their own. |
| 2. Degradable pollutants are usually acted upon by microorganisms to reduce them to inorganic substances. | 2. non-degradable pollutants are not acted upon by microorganisms and hence are not reduced to inorganic substances. |
| 3. Degradable pollutants are not accumulated in nature. | 3. non-degradable pollutants accumulate in nature and remain there for a long period of time. |
| 4. Degradable pollutants emit foul odour when they are being decomposed. | 4. non-degradable pollutants may not emit foul odour as they are not decomposed. |
| 5. Vegetables and fruits, food refuse, organic matter, etc. form degradable pollutants. | 5. Metals, plastic, glass, etc. form non-degradable pollutants. |
![]()
Question 2.
Industrial waste and Domestic waste:
| Industrial waste | Domestic waste |
| 1. Most of the industrial waste contains non-degradable pollutants. | 1. Most of the domestic waste contains bio-degradable pollutants. |
| 2. Industrial wastes are produced during industrial and manufacturing processes. | 2. Domestic wastes are produced in every home due to day to day activities. |
| 3. Pollution monitoring and controlling bodies like MPCB keep a watch on the proportion of industrial wastes. | 3. Pollution monitoring and controlling bodies like MPCB do not keep a watch on the proportion of domestic wastes. It is the individual responsibility of every citizen to reduce the amount of domestic waste that they produce. |
| 4. Fly ash from thermal power plants, heavy metals, chemicals, etc. form the industrial wastes. | 4. Garbage, domestic refuse, and discarded solid materials containing food waste, paper, cardboard, peels of fruits, vegetable matter, etc. form the domestic wastes. |
Give scientific reasons:
Question 1.
Domestic sewage is harmful for all forms of life.
Answer:
- Domestic sewage contains water
- There are detergents and washing private vehicles. powders containing phosphate, which are used to soften the water.
- These chemicals are harmful to aquatic animals.
- They also contain disease. causing pathogenic bacteria and viruses.
- Hence, domestic sewage is harmful for originating from kitchen, bathrooms, toilet, forms of
![]()
Question 2.
Use public transport instead of private vehicles.
Answer:
- All the automobiles use fossil used to soften the water. fuels Burning of fossil fuels causes air pollution by gaseous pollutants as well as by particulates.
- Toxic gases such as CO, CH4, SO2, etc. are emitted through automobile exhausts.
- When each person uses private vehicles, the proportion of air pollution increases.
- Instead, public transport helps to reduce air pollution it will also help to ease trafficams.
- Therefore, as a role of citizen in pollution control, public transport should be used instead of private vehicles.
Question 3.
Due to agriculture, there can be a lot of air pollution.
Answer:
- During agricultural practices, open field burning is done. Due to this burning there is emission of gases like SO2, CO2, CH4, CO and oxides of nitrogen along with large amounts of particulate matter.
- In agricultural practices, pesticides used emit toxic chemicals.
- Industrial farms pollute air by emitting foul odour and airborne pollutants.
- When manure is decomposed, there is production of greenhouse gases.
Question 4.
A hole has been observed in the ozone layer in the stratosphere near Antarctica.
Answer:
- Ozone layer depletion is mainly caused due to the action of CFC (Chlorofluorocarbon) molecules in the air.
- Due to various increased activities of humans, the magnitude of air pollution has been increasing in the last few decades.
- CFC molecules were used as coolants in refrigerators, freezers and air conditioners.
- They were also present in industrial solvents, dry cleaning agents and hospital sterilants, aerosols and foam. Due to such enhanced use, much of the CFCs were liberated in the last few years.
- CFC molecules are decomposed by ultraviolet rays which release chlorine and fluorine molecules.
- Chlorine and fluorine react with the ozone resulting in a hole in the ozone layer present in the stratosphere.
Therefore, a hole has been observed in the ozone layer in the stratosphere above Antarctica.
Answer the following.
Question 1.
What do you mean by ozone layer depletion? What are the causes of ozone layer depletion?
Answer:
1. The ozone layer is present at the top of the stratosphere. The stratosphere is the second layer of the atmosphere which is present 48 km above the earth’s surface.
2. Ozone layer is protective layer for living organisms of the earth, as it absorbs harmful UV rays from the sun. When this layer is reduced or destroyed, it is called ozone layer depletion.
3. Causes of the ozone layer depletion:
- The main cause of ozone depletion are CFC molecules.
- Chlorine atoms are present in chlorofluoro-carbons (CFC) molecules. They react with ozone and deplete it.
- CFCs are used as coolants in refrigerators, freezers and air conditioners manufactured before 1995.
- CFCs are also present in industrial solvents, dry cleaning agents and hospital sterilants (sterilizers), aerosols and foam. All the above materials release a lot of CFCs into the atmosphere.
- CFC molecules are broken down by ultraviolet radiations which result in release of chlorine and fluorine, which further reduce the ozone layer.
![]()
Question 2.
What adverse effect does ozone depletion have?
Answer:
- When the ozone layer is depleted, the ultraviolet radiations of the sun can reach the earth’s surface in greater proportion.
- This results in damage to animal and plant life on the earth.
- Ultraviolet rays cause skin cancer and cataract in human beings.
- The ozone hole is seen in the stratosphere above Antarctica.
Question 3.
Describe the effects of air pollution on animals and plants.
Answer:
1. Effects of air pollution on animals:
- Air pollutants affect breathing of the animals.
- Particulate pollutants can cause problems to the wildlife.
- Particulate matter containing heavy metals is accumulated in the bodies of animals. The accumulated heavy metals at high levels in the body tissues, can cause problems. ‘
- Acid rain causes serious problems to animal life.
2. Effects of air pollution on plants:
- Various parts of the plant show reduced growth after coming in contact with air pollutants.
- The leaves show yellowing or chlorosis on exposure to air pollutants.
Question 4.
What are man-made reasons for water pollution?
Answer:
The effluents and other substances released by man into the surrounding water bodies together can be called man-made reasons for water pollution.
1. Domestic sewage: The excreta, urine and other domestic-use water is added to the water bodies in many cities and villages. In big metro-cities, the sewage is partially treated but these management practices are not enough.
2. Industrial effluent: Different industries and factories release effluents which may contain toxic and harmful components, such as various pigments, bleaching chemicals, leather pieces, fibres, mercury, lead, etc.
3. Oil pollution: Oil spillages are seen in the seas due to leakage of crude oil. The crude oil is hazardous as it contains cancer causing hydrocarbons.
4. Fertilizers and pesticides: These compounds when used in farm, may get washed off to nearby water body. The chemical fertilizer containing N, P, K cause water pollution. Pesticides such as endrin, chlorine, carbonate containing pesticides, etc. are mixed with water. They cause contamination of the aquatic animals.
5. The wrong behaviour of human beings causes water pollution. The addition of wastes, defecation near coasts, washing clothes, decomposing hemp and flax in water, disposal of ashes, floral offerings to god, dumping ashes all such activities result into water pollution.
6. The warm water released into the water body through thermal power plants cause thermal pollution.
![]()
Question 5.
What are the effects of water pollution on human beings?
Answer:
The water-borne diseases that are caused by different bacteria and viruses cause infections to human beings through contaminated water. Some bacterial and viral diseases are spread through epidemics. Cholera, hepatitis, enteritis, diarrhoea, typhoid are such diseases that can cause severe infections to man. Polluted water also cause skin diseases and deformities of bones, Some pollutants accumulated in vital organs cause their ailments. Liver, kidneys, brain, etc. are affected in this way. Person may develop hypertension too due to pollutants.
Question 6.
What are the effects of water pollution on the ecosystem?
Answer:
Biological effects:
- Plants in the ecosystem show retarded growth, resulting into species loss.
- Due to imbalance in the ecosystem, the food chain and food web is disturbed.
- Pollutants cause mortality in fish and other aquatic animals.
- Oil slick causes harmful impact on the marine birds.
- Useful bacterial fauna in the water is lost.
Abiotic effects:
- Pollutants cause changes in physical and chemical properties of water.
- Salinity of the water changes.
- Dissolved oxygen in the water is depleted, causing mortality of fishes.
Question 7.
Describe the effects of air pollution on the environment.
Answer:
Air pollution can cause the following serious effects on the environment:
- Deforestation and fuel consumption bring about rise in CO2 concentration.
- Excess CO2 in air causes rise in atmospheric temperature of the earth.
- The increased temperature is called global warming.
- The global warming results into melting of glaciers, subsequently causing rise in the sea level.
- There is a change in the climate and pattern of rainfall. This may indirectly affect the agricultural production.
![]()
Question 8.
Describe the effects of soil pollution.
Answer:
Effect of soil pollution:
- There are many pathogenic bacteria, viruses and parasitic intestinal worms in the sewage sludge. These are able to cause many diseases.
- Soil and vegetable crops are contaminated by manure made from human and animal excreta containing pathogens. This can lead to various diseases.
- There is loss of fertility and productivity of soil and land due to soil pollution.
- Soil pollution leads to water pollution, when toxic chemicals leach into the groundwater. Similarly, when contaminated soil enters into streams or lakes, it also causes water pollution.
- Radioactive materials and soil contaminants can travel through food chains. They move away from the soil into crops, livestock and human bodies.
Question 9.
How do biodegradable and non- biodegradable wastes cause land pollution?
Answer:
- Biodegradable material is mainly present in the domestic waste.
- It is in the form of food waste, peels of fruits, vegetables, etc.
- Paper is also a main part of the domestic waste which is biodegradable.
- Polythene bags, plastic waste and footwear, etc. are non-biodegradable waste from the domestic sources. All of these pollute the land.
Question 10.
How do you protect soil from being polluted?
Answer:
- We should not throw domestic waste and industrial waste indiscriminately on the land, so that it contaminates soil.
- Proper disposal of solid wastes and more importantly safe disposal of biomedical waste material should be practised.
- Instead of throwing non-biodegradable materials on the land, they should be properly recycled and reused.
- Biodegradable materials should be composted and converted into useful manure, rather than throwing them to cause pollution of the soil.
- Excessive use of fertilizers and pesticides should be avoided so that the soil does not get contaminated.
![]()
Question 11.
What are the different laws to prevent pollution?
Answer:
The different laws to prevent pollution are as follows:
- Water (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Act, 1974.
- Air (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Act, 1981.
- Environment (Protection) Act, 1986.
- There are different laws and rules which have been made for the disposal of hazardous waste, biomedical waste, solid waste and prevention of noise pollution.
Question 12.
Who implements the laws related to pollution?
Answer:
The Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) and Maharashtra Pollution Control Board (MPCB) check whether the organizations like factories, industrial estates, Municipalities, Zilla Parishads, Panchayat Samities and Gram Panchayats follow all the laws related to control of pollution.
Use your brain power!
Question 1.
Which types of pollutants are observed?
Answer:
Pollutants are of many varied types. They can be classified according to their sources, according to which ecosystem they are polluting, and according to their characteristics.
Question 2.
Whether the pollutants are degradable or non-degradable?
Answer:
Some pollutants are biodegradable while some are non-biodegradable. The pollutants that spread in the air are in the form of gases or particulate matter. Though they are non-degradable, they constantly make chemical reactions with each other.
The pollutants thrown in water and on land are of both the types. Pollutant like plastic is totally non-biodegradable. The biodegradable substances can be decomposed by various bacteria and fungand are converted back into elemental form. The pollutants added in S the water are also of two types. The heavy metals and colours are non-degradable.
![]()
Think about it:
Question 1.
If natural materials are pollutants, why do we not perceive their adverse effects during their use? When such materials are referred as pollutants?
Answer:
The natural pollutants are active only for a short duration. Due to natural reasons their activity is limited, and they are lost after a specific time. Their sources are not continuous and their spread too is not regular as in case of man-made pollutants which are emitted steadily.
Thus, we can avoid these substances. We also use them in limited quantity. Therefore, the natural substances, though may be polluting in nature, we are unable to perceive its toxicity. However, if we use them in abundance and create an imbalance, then its effect can be experienced as a great hazard.
Question 2.
What are the reasons other than those mentioned on the textbook page no. 55 mentioned responsible for air pollution?
Answer:
1. The automobile vehicles like two-wheelers and four-wheelers are increasing tremendously in numbers. This uncontrolled number of vehicles and their heavy traffic is causing air pollution to very high level in megacities.
2. Construction industries, demolition of the old buildings, digging the roads, are such activities which are adding to the particulate air pollution of the cities.
3. The bursting of firecrackers on the occasion of festivals and ceremonies, the spread of gulal during processions are also actions which result into unwanted air pollution.
4. Aeroplane traffic, rocket launching, industrial farming are the modern sources of air pollution.
![]()
Question 3.
Whether the vehicles with two- stroke engine cause more pollution than four stroke engine?
Answer:
Yes, they do. Scooters and motor cycles are more dominant source of air pollution as they emit soot and organic particles. In urban areas this proportion is high. These particles are toxic and they create heavy air pollution.
The two-wheelers have two-stroke engines. Such engines are far less efficient in burning the fuel that is used in the vehicles. The exhaust systems are also less effective at removing pollutants. On the contrary most of the four-wheelers have catalytic converters. Therefore, the exhaust fumes from scooters contain higher levels of the chemicals found in the fuel and oil they use.
The vehicles with two-stroke engine such as two wheelers emit significantly more primary organic aerosols and volatile organic compounds from incomplete burning of the fuel. They also produce significant secondary organic aerosols as gases released from the exhaust react with the air and microscopic particles of soot.
These pollutants increase the risk of heart and lung disease. Older two-stroke vehicles produced reactive oxygen molecules that are known to be potentially harmful for lung health. In recent times there is excessive use of two-wheelers which is deteriorating the air quality to great extent.
Question 4.
Give 5 examples of each of domestic waste, biological waste and agricultural waste and write in your own words about soil pollution due to those wastes.
Answer:
Domestic waste:
- Empty containers of medicines, papers, bottles, etc.
- Plastic
- Glass pieces
- Old utensils, clothes
- Tins and cartons of used items, the discarded household items.
Biological waste:
- Dead corpse of animals.
- Urine and faeces
- Peels of fruits, stalks of vegetables and fruits.
- Food waste
- Garlands and old bouquets.
Agricultural waste:
- The stubs of crops after the grains are removed.
- Cattle dung and urine
- Some persistent amount of insecticides
- Some amount of fertilizers
- Empty containers, bags, cartons of insecticide, chemical fertilizers, seeds, gunny bags, etc.
![]()
Diagram based questions:
Question 1.
Given below is a diagram showing hazardous polluting event.
Explain what is this and what are its effects shown in the diagram.
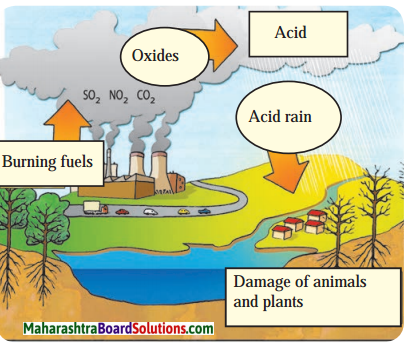
Answer:
The above picture depicts the formation and effects of acid rain. The toxic gases such as SO2 , CO2 and NO2 are released through the chimneys of factories. These oxides are released in air. They get dissolved in the rainwater and reach back the earth’s surface in the form of acids. The plants, animals and houses are being damaged due to this acid rain.
![]()
Question 2.
Draw a well labelled diagram to show greenhouse effect.
Answer:
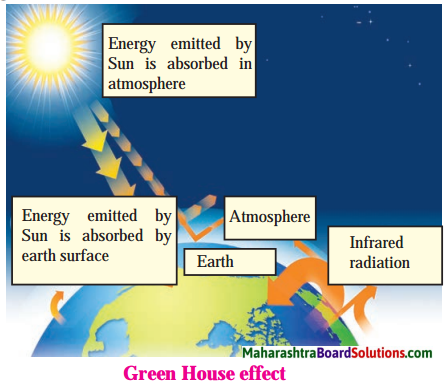
Activity based questions:
Question 1.
Discuss the issues like ‘dry waste-wet waste’ and ‘toilet in each home’ and write information in your own words.
MCQs based on practical:
Question 1.
Which fertilizers when used in excessive amounts cause soil pollution that spreads to neighbouring water bodies and cause water pollution too?
(a) Chemical
(b) Organic
(c) Artificial
(d) Compost
Answer:
(a) Chemical
![]()
Question 2.
What is the type of pollutants that are present in the industrial effluents that is released in the rivers and sea?
(a) Inorganic
(b) Organic
(c) Biological
(d) Biomedical
Answer:
(a) Inorganic
Question 3.
What grows in excess when eutrophication of the water bodies take place?
(a) Plants
(b) Algae
(c) Fishes
(d) Fungi
Answer:
(b) Algae
Question 4.
Which of the following is seen in the polluted water body?
(1) flowers used in pooja
(2) fruits
(3) fishes
(4) aquatic insects
(5) plastic bags
(6) turtles
(7) thick growth of algae
(8) light blue colour of water
(9) cattle wading in water
(10) broken idols
(a) (1) (3) (5) (6) (9) (10)
(b) (1) (2) (5) (7) (9) (10)
(c) (1) (3) (6) (8) (9) (10)
(d) (1) (2) (4) (7) (8) (9)
Answer:
(b) (1) (2) (5) (7) (9) (10)
Question 5.
Which is the easiest method to identify the polluted water?
(a) To taste the water
(b) To check the depth of water
(c) To observe colour and odour of the water
(d) To swim in the water
Answer:
(c) To observe colour and odour of the water
![]()
Formative Evaluation:
Question 1.
Which factors are responsible for pollution shown in the following pictures?

Question 2.
Compare the two neighbouring photographs.

Balbharati Maharashtra State Board 8th Std Science Textbook Solutions
- Living World and Classification of Microbes Class 8 Science Textbook Solutions
- Health and Diseases Class 8 Science Textbook Solutions
- Force and Pressure Class 8 Science Textbook Solutions
- Current Electricity and Magnetism Class 8 Science Textbook Solutions
- Inside the Atom Class 8 Science Textbook Solutions
- Composition of Matter Class 8 Science Textbook Solutions
- Metals and Nonmetals Class 8 Science Textbook Solutions
- Pollution Class 8 Science Textbook Solutions
- Disaster Management Class 8 Science Textbook Solutions
- Cell and Cell Organelles Class 8 Science Textbook Solutions