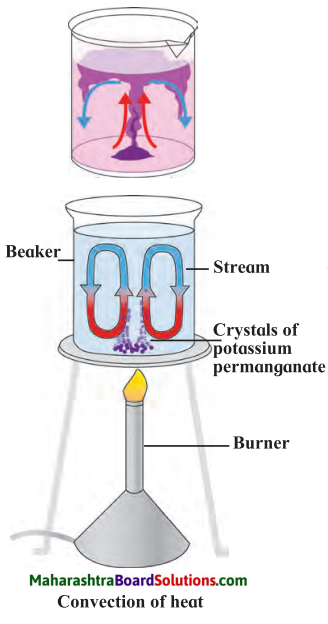
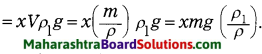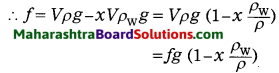Std 6 Science Chapter 13 Sound Question Answer Maharashtra Board
Balbharti Maharashtra State Board Class 6 Science Solutions Chapter 13 Sound Notes, Textbook Exercise Important Questions and Answers.
Class 6 Science Chapter 13 Sound Question Answer Maharashtra Board
1. Fill in the blanks with the proper words.
Question a.
The propagation of sound does not occur through a ………….. .
Answer:
vacuum
![]()
Question b.
Noise pollution is a …………… issue.
Answer:
social/serious
Question c.
The sound which is disagreeable to our ears is called …………… .
Answer:
noise
Question d.
Noise has adverse effects on our …………….. .
Answer:
health
2. What should we do?
Question a.
The silencer of a motorcycle is broken.
Answer:
- If the silencer of a motorcycle is broken, vehicle should be immediately taken to the garage for repair.
- If silencer is not maintained properly, it will continue making loud noise on the road while in motion, resulting in increasing noise pollution.
![]()
Question b.
A factory in the surrounding is producing continuous loud noise.
Answer:
Factories should be located at a proper distance away from residential areas. Authorities should be contacted who will control the decibel level.
3. Write the answers in your own words.
Question a.
What is meant by vibration?
Answer:
Vibration of an object is necessary for the production of sound. As long as the object vibrates, the sound is heard. When the vibration stops, the sound also stops.
Question b.
Explain with the help of practical examples how sound is propagated through solids.
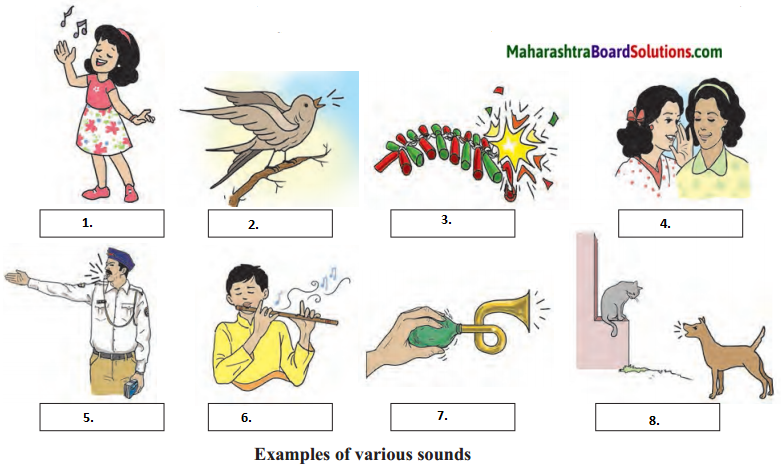
Answer:
- Singing
- Chirping of birds
- Bursting of crackers
- Whispering
- Whistling
- Flute
- Honking
- Dog barking
![]()
Question c.
What is meant by noise pollution?
Answer:
Continuous noise which has ill effects is called noise pollution.
Question d.
What measures will you take to control noise pollution?
Answer:
Measures for preventing noise pollution:
- As far as possible, we should avoid blowing horns.
- The volume of the TV or radio in the house should be restricted to those watching the programmes.
- Vehicles should be maintained properly to reduce the unnecessary sounds they produce.
- Factories, airports, railway stations and bus stands should be located at the proper distance away from residential area.
- Planting of trees helps reduce noise as trees act as a natural barrier.
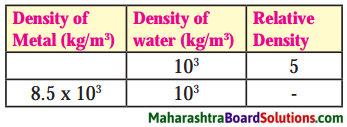
4. Complete the table.
Question a.
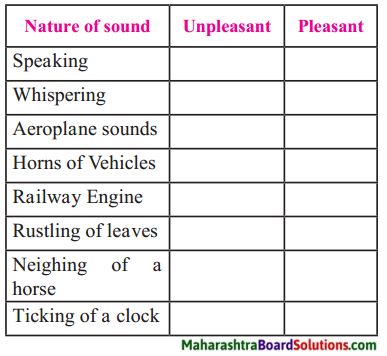
Answer:
| Nature of sound | Unpleasant | Pleasant |
| 1. Speaking | ✓ | |
| 2. Whispering | ✓ | |
| 3. Aeroplane Sounds | ✓ | |
| 4. Horns of Vehicles | ✓ | |
| 5. Railway Engine | ✓ | |
| 6. Rustling of leaves | ✓ | |
| 7. Neighing of a horse | ✓ | |
| 8. Ticking of a clock | ✓ |
Project:
Question 1.
Prepare a list of the harsh sounds mheard near your house. Write about those sounds which produce noise pollution.
![]()
Question 2.
Collect information about places where loud noise is prohibited and discuss why it is so.
Class 6 Science Chapter 13 Sound Important Questions and Answers
Fill in the blanks:
Question 1.
Some sounds are ……………… and are heard easily.
Answer:
loud
Question 2.
Some sounds are very ……………… and cannot be heard unless we listen attentively.
Answer:
soft
Question 3.
As long as the object ……………… the sound is heard.
Answer:
vibrates
Question 4.
When the vibration ……………… the sound also stops.
Answer:
stops
![]()
Question 5.
The intensity of sound is measured in a unit called ……………… .
Answer:
decibels(dB)
Question 6.
The voice box is located in our ……………… .
Answer:
throat
Question 7.
Sound travels in the form of ……………… through air, water and ……………. .
Answer:
waves, solids
Question 8.
The sound is propagated more clearly through a ……………… than through air.
Answer:
solid
Question 9.
Transmission of sound occurs at a different ……………… through different mediums.
Answer:
speed
![]()
Question 10.
Continuous noise which may have ill effects, is called noise ……………… .
Answer:
pollution
Question 11.
Some of the sounds that we enjoy can be a ……………… for others.
Answer:
nuisance
Question 12.
The vibration of an object is necessary for the ……………… of sound.
Answer:
production
Answer in one sentence.
Question 1.
List characteristics of sound.
Answer:
Sounds are soft, loud, pleasant and unpleasant.
![]()
Question 2.
What do you mean by unpleasant sounds?
Answer:
The sounds by which we get annoyed are called unpleasant sounds.
Question 3.
What do you mean by loud and soft sounds?
Answer:
The sounds which are heard easily, are loud sounds and the sounds which cannot be heard unless we listen attentively, are soft sounds.
Question 4.
Which movement is exhibited by diaphragm of a speaker and a tabla?
Answer:
Diaphragm of a speaker and a tabla exhibit rapid oscillatory motion which gives rise to vibrations.
Question 6.
What is source of the sound?
Answer:
The object due to which sound is produced is called the source of the sound.
![]()
Question 7.
What is acoustics?
Answer:
The science of sound, resonance, production, propagation and effects of sound is called acoustics.
Question 8.
What produces sound in living beings?
Answer:
The vibration of the vocal chords in our larynx or voice box produces sound.
Question 9.
On what does quality of sound depend?
Answer:
Quality of sound produced in the larynx depends upon the tautness of the vocal chords.
Question 10.
How is sound propagated?
Answer:
The sound is propagated in the form of waves through air, water or through a solid.
Question 11.
Why is sound heard more clearly through solids?
Answer:
Transmission of sound occurs at a different speed through different mediums. Transmission of sound is faster through a solid than through a liquid and gas.
![]()
Question 12.
What is noise?
Answer:
A loud sound is harsh to ears. Such sounds produce noise.
Question 13.
List the effects of very loud or continuous noise on the people.
Answer:
- Very loud or continuous noise can cause hearing impairment.
- This can even lead to deafness.
- It also causes restlessness, irritability and mental exhaustion.
Question 14.
What is noise pollution?
Answer:
Continuous noise which has ill effects is called noise pollution.
![]()
Question 15.
How can we prevent noise pollution with respect to watching TV?
Answer:
The volume of the TV or radio in the house should be restricted to those watching the programmes.
Explain the terms.
Question 1.
Propagation of sound:
Answer:
Sound is said to be propagated when sound waves spread in all directions from a source of sound.
Question 2.
Medium of propagation of sound:
Answer:
The substance around a source of sound through which sound waves spread is called the medium of propagation of sound.
Question 3.
Which sounds do you hear during the recess in the school?
Answer:
During the recess in the school, we hear.
- laughing
- students running
- talking loudly
- ringing of the bell
- stamping on the staircase
- shouting
![]()
Question 4.
When there is silence in the classroom, close your eyes and sit quietly. Which sounds in your surroundings can you hear now?
Answer:
- Loud: Laughing, running, talking, horn of cars, marriage procession, school band, teacher’s voice in next classroom.
- Pleasant: P.T. teacher’s whistle, chirping of birds.
- Unpleasant: Shouting, bell ringing, stamping on staircase, dog barking, horns of vehicles.
Question 5.
When a song is being played on a radio or a music system in the house, place your hand on its speaker. What do you feel? Put off the music. What do you feel now?
Answer:
- When a hand is placed on the speakers of the music system, we feel vibrations on the hand.
- When music is put off, we don’t feel any vibrations on the hand.
Question 6.
When a metal dish falls on the floor; it makes a loud noise. What do we do to stop the noise? What is the effect of that action?
Answer:
To stop the noise of metal dish falling on the floor, quickly put hand on the dish. Vibrations of the metal dish are stopped and the noise stops.
![]()
Question 7.
What is it that vibrates when the sounds of sitar, bell, water tap, and breaking of a saucer, etc. are produced?
Answer:
Strings of the sitar, tongs of the bell, water drops hitting the floor of the basin, pieces of saucers that hit the ground vibrate to produce the sounds.
Question 8.
Take a pot full of water. Strike it lightly on the rim. What do you see? Why are waves formed on the water in the pot?
Answer:
- We see ripples on the water.
- When we strike the rim of the pot, our striking causes vibrations. These vibrations are transferred or moved from the pot to the water. Hence, water waves/ripples are seen on the water in the pot.
Question 9.
On rubbing balloon filled with water and another filled with air, of which balloon do we hear a clear or sound?
Answer:
We hear a clearer sound of the water balloon.
Question 10.
If a bell is rung in a vacuum container, will its sound be heard outside?
Answer:
Its sound will not be heard outside.
Observe and Discuss.
Observe the figure and answer the questions.
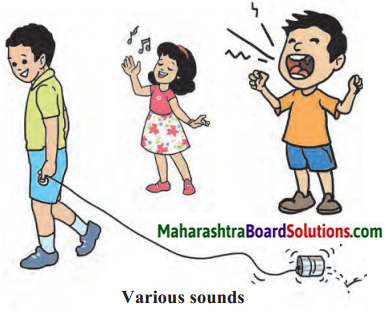
Question 1.
Which of these sounds is pleasant?
Answer:
The singing of the girl is a pleasant sound.
![]()
Question 2.
Which sound is a nuisance to people?
Answer:
- Boy shouting/screaming.
- Boy moving/ walking with a toy rattle.
Observe the figure and answer the following.
Question 1.
Make a list of all sounds implied in the picture.
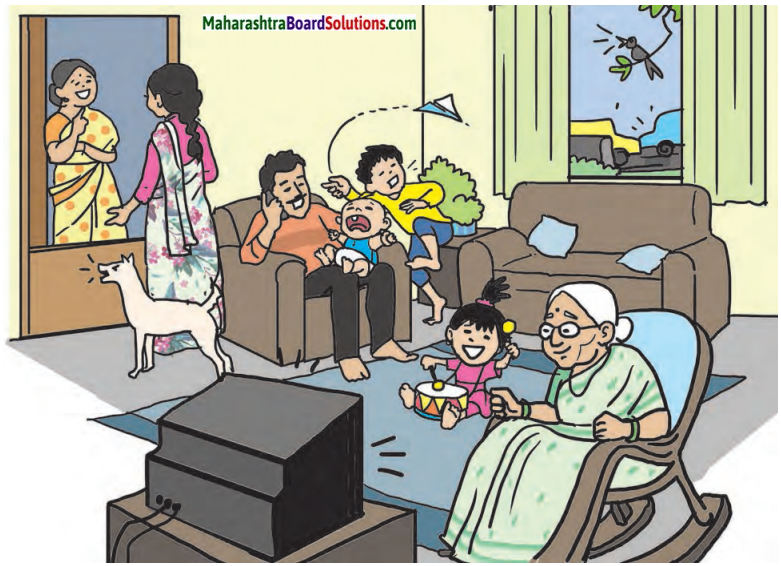
Answer:
- Chirping of bird outside the house on the tree.
- Collision of two vehicles – honking of the vehicles.
- Baby crying.
- Father talking on the phone.
- Brother playing in the house – jumping.
- Sister playing the drum – hitting the drum.
- Sound of TV.
- Dog barking.
- Mother talking to the neighbour.
Question 2.
How would this atmosphere affect a person who is not feeling well?
Answer:
This atmosphere is not convenient for a patient who is ill. He cannot take rest.
![]()
Question 3.
Would you be able to study in these conditions?
Answer:
No, students cannot study in this condition. They cannot concentrate on their study.
Maharashtra State Board Class 6 Science Textbook Solutions
- Work and Energy Class 6 Science Textbook Solutions
- Simple Machines Class 6 Science Textbook Solutions
- Sound Class 6 Science Textbook Solutions
- Light and the Formation of Shadows Class 6 Science Textbook Solutions
- Fun with Magnets Class 6 Science Textbook Solutions
- The Universe Class 6 Science Textbook Solutions