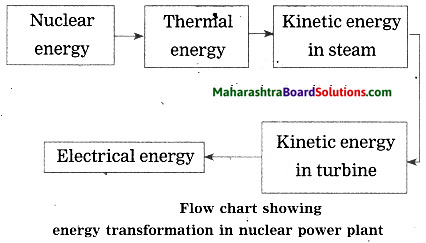
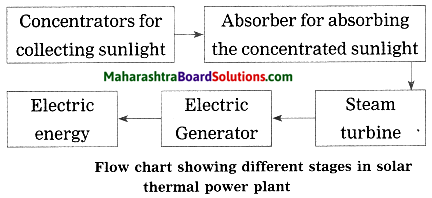
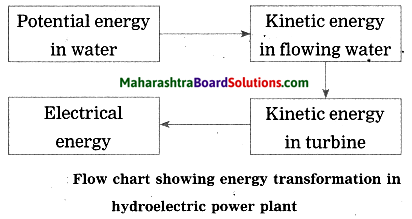
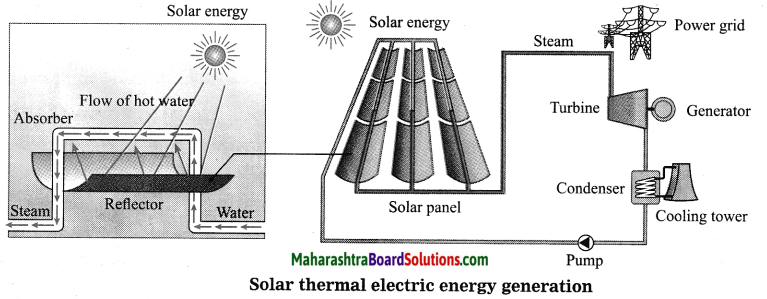
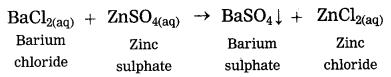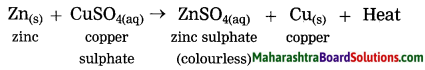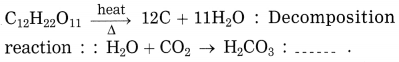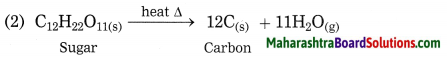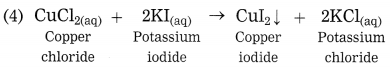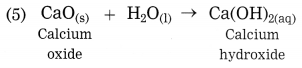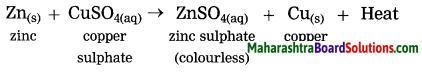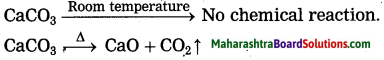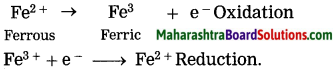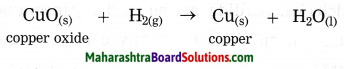Balbharti Maharashtra State Board Class 10 Science Solutions Part 1 Chapter 8 Metallurgy Notes, Textbook Exercise Important Questions and Answers.
Maharashtra State Board Class 10 Science Solutions Part 1 Chapter 8 Metallurgy
Question 1.
a. Alloy of sodium with mercury.
Answer:
Silver amalgam.
b.Molecular formula of common ore of aluminium.
Answer:
Al2O3.nH2O
c. The oxide that forms salt and water by reacting with both acid and base.
Answer:
Aluminium oxide (Al2O3).
d. device used for grinding an ore.
Answer:
The device used for grinding an ore is grinding mill.
e. The nonmetal having electrical conductivity.
Answer:
Graphite having electrical conductivity.
f. The reagent that dissolves noble metals.
Answer:
Aqua regia is the reagent that dissolves noble metals like gold and platinum.
![]()
Question 2.
Make pairs of substances and their properties.
| Column I | Column II |
| Substance | Property |
| (1) Potassium bromide | (a) Combustible |
| (2) Gold | (b) Soluble in water |
| (3) Sulphur | (c) No chemical reaction |
| (4) Neon | (d) High ductility |
| (e) Magnetic ingredient |
Answer:
(1) Potassium bromide – Soluble in water
(2) Gold – High ductility
(3) Sulphur – Combustible
(4) Neon – No chemical reaction
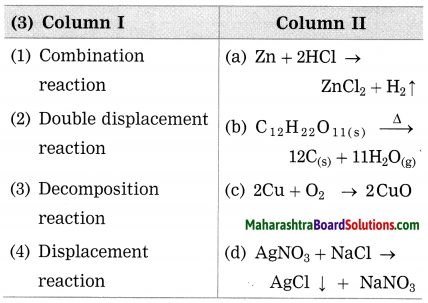
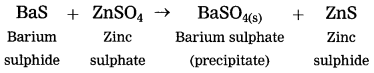
Question 3.
Identify the pairs of metals and their ores from the following.
| Column I (ores) | Column II (metals) |
| (1) Bauxite | (a) Mercury |
| (2) Cassiterite | (b) Aluminium |
| (3) Cinnabar | (c) Tin |
| (d) Copper |
Answer:
(1) Bauxite – Aluminium
(2) Cassiterite – Tin
(3) Cinnabar – Mercury
Question 4.
Explain the terms.
a. Metallurgy
Answer:
Metallurgy: The process used for extraction of metals in their pure form from their ores, then metals are further purified by different methods of purification. All the process is called metallurgy.
b. Ores.
Answer:
Ores: The minerals from which metals are extracted profitably and conveniently are called ores.
Examples: Bauxite (Al2O3.H2O), Cinnabar (HgS).
c. Minerals.
Answer:
Minerals: The naturally occurring compounds of metals along with other impurities are known as minerals.
Examples: Rocks are composed of mixtures of minerals. Talc and granite are minerals.
d. Gangue.
Answer:
Gangue: Ores contain metal compounds with some of the impurities like soil, sand, rocky material, etc. These impurities are called gangue.
![]()
Question 5.
Write scientific reasons.
a. Lemon or tamarind is used for cleaning copper vessels turned greenish.
Answer:
- Copper undergoes oxidation in air to form black copper oxide. Copper oxide reacts slowly with carbon dioxide in air and gains a green coat. This green substance is copper carbonate.
- Lemon and tamarind contain acid. The acid dissolves the green coating of basic copper carbonate present on the surface of a tarnished copper utensil and makes it shiny again.
b. Generally the ionic compounds have high melting points.
Answer:
- The ionic compounds exist in solid state and are hard due to strong electrostatic force of attraction between oppositely charged ions.
- The intermolecular force of attraction is high in ionic compounds and large energy is required to overcome it. Therefore, ionic compounds have high melting points.
c. Sodium is always kept in kerosene.
(OR)
Why is sodium stored in kerosene?
Answer:
- Sodium reacts so vigorously with atmospheric oxygen that it catches fire if kept in the open.
- It does not react with kerosene and sinks in it. Hence, to protect sodium and to prevent accidental fires it is always kept in kerosene.
d. Pine oil is used in the froth floatation process.
Answer:
- In the concentration of an ore by froth floatation process, the ore is mixed with water and pine oil. When air is bubbled through the mixture a froth is formed.
- The mineral particles in the ore are preferentially wetted by the oil and float on the top in the froth.
- The gangue particles are wetted by water and settle down. Thus the mineral can be separated from the gangue and the ore is concentrated.
e. Anodes need to be replaced from time to time during the electrolysis of alumina.
Answer:
- During electrolysis of alumina, the oxygen liberated at the carbon anode reacts with graphite rods (carbon anode) and forms carbon dioxide.
- As the anodes get oxidised during electrolysis of alumina, they are continuously eroded. Hence, it is necessary to replace anodes from time to time.
Question 6.
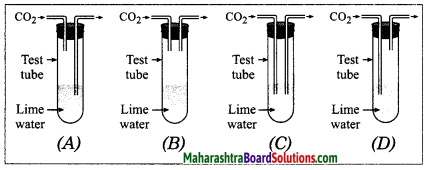
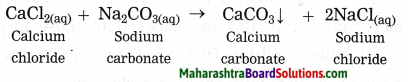
When a copper coin is dipped in silver nitrate solution, a glitter appears on the coin after some time. Why does this happen? Write the chemical equation.
Answer:
When a copper coin is dipped in a silver nitrate solution, more reactive copper displaces silver from silver nitrate solution. The silver so liberated deposits on the copper coin. As a result, a shiny coat of silver is formed on the coin.
Cu(s) + 2AgNO3(aq) → Cu(NO3)2(aq) + 2Ag(s)
![]()
Question 7.
The electronic configuration of metal ‘A’ is 2, 8, 1 and that of metal ‘B’ is 2, 8, 2. Which of the two metals is more reactive? Identify these metals. Write their reaction with dilute hydrochloric acid. (Practice Activity Sheet – 1)
Answer:
If the number of electrons in the outermost orbit is less, then the metal is more reactive. Metal A contains one electron in the outermost shell, while metal B contains two electrons. Hence, metal A is more reactive than metal B.
Metal A is sodium and metal B is magnesium. Reactions of Na and Mg with dil. HCl are,

Question 8.
Draw a neat labelled diagram.
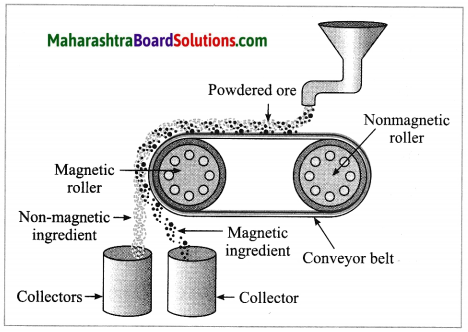
a. Magnetic separation method.
Answer:
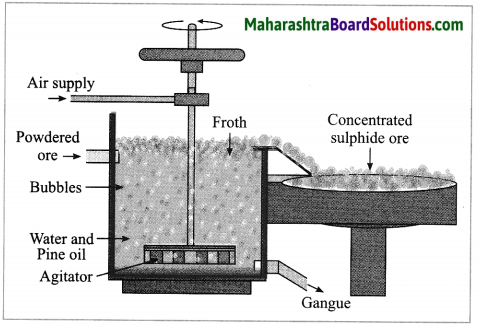
b. Forth floatation.
Answer:
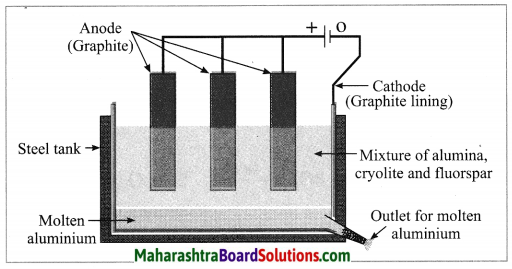
c. Electrolytic reduction of alumina.
Answer:
d. Hydraulic separation method.
Answer:
![]()
Question 9.
Write chemical equation for the following events.
a. Aluminium came in contact with air.
Answer:
When aluminium is exposed to air, it develops a thin oxide layer of aluminium.
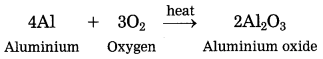
b. Iron filings are dropped in aqueous solution of copper sulphate.
Answer:
When iron filings are dropped in copper sulphate solution, more reactive iron displaces copper from copper sulphate solution. The iron filings get coated with reddish brown copper metal and the blue colour of copper sulphate fades gradually and ferrous sulphate is formed.
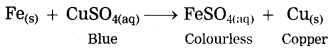
c. A reaction was brought about between ferric oxide and aluminium.
Answer:
The reaction between ferric oxide and iron produces aluminium oxide and iron. It is a thermite reaction and is highly exothermic.
It produces a large amount of heat, which is released to melt oxygen and aluminium. This reaction is used in welding of machineries. It is also used in warfare to make grenades.
The chemical reaction for the above is as follows:
3Fe3O2 + 4Al → 2Al2O3 + 6Fe
d. Electrolysis of alumina is done.
Answer:
During electrolysis of alumina, aluminium is deposited at the cathode. Molten aluminium being heavier than the electrolyte, is collected at the bottom of the tank. Oxygen gas is liberated at the anode.
Anode reaction: 2O–– → O2 + 4e– (Oxidation)
Cathode reaction: Al3+ + 3e– → Al(l) (Reduction)
e. Zinc oxide is dissolved in dilute hydrochloric acid.
Answer:
Zinc oxide is dissolved in dilute hydrochloric acid, zinc chloride and water are formed.

Question 10.
Complete the following statement using every given options.
During the extraction of aluminium
a. Ingredients and gangue in bauxite.
b. Use of leuching during the concentration of ore.
c. Chemical reaction of transformation of bauxite into alumina by Hall’s process.
d. Heating the aluminium ore with concentrated caustic soda.
Answer:
c. Chemical reaction of transformation of bauxite into alumina by Hall’s process.
![]()
Question 11.
Divide the metals Cu, Zn, Ca, Mg, Fe, Na, Li into three groups, namely, reactive metals, moderately reactive metals and less reactive metals.
Answer:
Reactive metals: Na, Li, Ca
Moderately reactive metals: Zn, Fe, Mg,
Less reactive metals: Cu
Project: (Do it your self)
Collect metal vessels and various metal articles. Write detailed informciton. write the steps in the procedure that can be done in the laboratory for giving glitter to these. Seek guidance from your teacher.
Can you recall? (Text Book Page No. 93)
Question 1.
what are the physical properties of metals and nonmetals?
Answer:
Properties of metals:
- Solid state (Exception: Mercury and gallium)
- Typical lustre
- Malleability and ductility
- Hardness (Exception: Lithium, sodium and potassium)
- Good conductors of heat and electricity
- High melting and boiling points (On the other hand, the melting and boiling points of the metals sodium, potassium, mercury and galium are very low.)
- Sonorous and produce sound on striking a hard surface.
Properties or nonmetals:
- Gaseous or solid state (Exception: Bromine in liquid state)
- Lack of any typical lustre (Exception: Iodine and Diamond)
- Brittleness in the solid state (Exception: Diamond is the hardest natural substance)
- Bad conductors of heat and electricity (Exception: Graphite) (Diamond is good conductor of heat)
- Low melting and boiling points.
Can you recall? (Text Book Page No. 102)
Question 1.
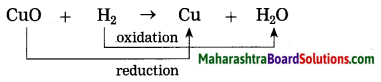
What is the electronic definition of oxidation and reduction?
Answer:
When a metal loses çlectrons the process is called an oxidation while when a nonmetal gains electrons, it is called a reduction,
Na → Na+ + e– (oxidation)
Cl– + e– → Cl (reduction)
![]()
Can you recall? (Text Book Page No. 106)
Question 1.
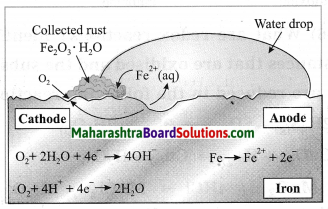
What is meant by corrosion?
Answer:
Corrosion is degradation of a material due toreaction with its environment.
Question 2.
Have you observed the following things?
(1) Old iron bars in the builthngs.
Answer:
When old iron bars in the buildings are exposed to moist air for a long time, they acquire a coating of browm nlaky substance called rust. (Fe2O3.H2O)
(2) Copper vessels not cleaned for a long time.
Answer:
If copper vessels are not cleaned for a long time, they react with moist carbon dioxide in the air, lose their shine and gain a green coat of copper carbonate. (CuCO3)
Question 3.
Silver ornaments or idols exposed to air for a long time.
Answer:
When silver ornaments or idols are kept exposed to air for a long time, silver reacts with sulphur in the air to form a coating of black silver sulphide. (Ag2S)
Question 4.
Old vehicles fit to be thrown away.
Answer:
The metallic parts of the body of old cars are corroded, eaten up and sometimes become perforated. The old cars also lose the original colour due to formation of flakes of rust.
Use your brain power! (Text Book Page No. 98)
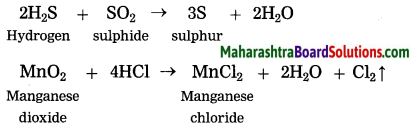
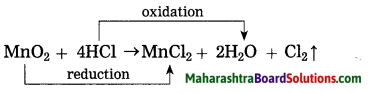
Question 1.
In the reaction between chlorine and HBr a transformation or HBr into Br2 takes place. Can this transformation be called oxidation? What Is the oxidant that brings about this oxidation?
Answer:
The conversion of HBr to Br2 is an oxidation process. In the above reaction, Cl2 in the oxidant.
![]()
Can you tell? (Text Book Page No. 104)
Question 1.
what are the moderately reactive metals?
Answer:
In the middle of the reactivity series, metals such as iron. zinc, lead, copper are moderately reactive.
Question 2.
In which form to the moderately reactive metals occur in nature?
Answer:
The moderately reactive metals which occur in nature are in the form of their sulphide salts or carbonate salts.
Think about it (Text Book Page No. 106)
Question 1.
Why do silver articles turn blackish while copper vessels turn greenish on keeping in air for long time?
Answer:
- Silver articles turn blackish on exposure to air for a long time. This is because of silver sulphide (Ag2S) laver formed on the silver articles by the reaction of silver with hydrogen sulphide.
- Carbon dioxide in moist air reacts with copper vessel. Copper loses its lustre due to formation of greenish layer of copper carbonate (CuCO3) on its surface.
Question 2.
Why do pure gold and platinum always glitter?
Answer:
Gold and platinum are noble metals as they do not react with moisture, O2 and CO2 from air also acids and alkalis, therefore, pure gold and platinum always glitter.
Use your brain power! (Text Book Page No. 103)
Question 1.
Write the electrode reaction for electrolysis of molten magnesium chloride and calcium chloride.
Answer:
(1) Magnesium chloride (MgCl2):
MgCl2 → Mg2+ + 2Cl–
At the cathode: Mg2+ + 2e– → Mg
At the anode: 2Cl– → Cl2 + 2e–
(2) Calcium chloride (CaCl2):
At the cathode: Ca2+ + 2e– → Ca
At the anode: 2Cl– → Cl2 + 2e–
![]()
Can you tell? (Text Book Page No. 106)
Question 1.
Which measures would you suggest to stop the corrosion of metallic articles or not allow the corrosion to start?
Answer:
Various types of methods are used to protect metals from corrosion. Almost in all the methods, special attention is paid so that iron does not rust. It is possible to lower the rate of the process of rusting of iron. Corrosion of metals can be stopped by detaching the air from metals.
Some methods are as follows :
- To fix a layer of some substance on the metal surface so that the contact of the metal with moisture and oxygen in the air is prevented and no reaction would occur between them.
- To prevent corrosion of metals by applying a layer of paint, oil, grease or varnish on their surface. For example, corrosion of iron can be prevented by this method.
Question 2.
What is done so to prevent rusting of iron windows and iron doors of your house?
Answer:
To prevent rusting of iron windows and iron doors in the house, they are painted so that they do not rust.
Question 3.
What is done so to prevent rusting or iron windows and iron doors of your house?
Answer:
To prevent rusting of iron windows and iron doors in the house, they are painted so that they do not rust.
Use your brain power! (Text Book Page No. 107)
Question 1.
Can we permanently prevent the rusting of an iron article by applying a layer of paint on its surface?
Answer:
The method of painting is alright for some time. We cannot protect the articles permanently from rusting by painting them.
Question 2.
Why do new iron sheets appear shiny?
Answer:
The new iron sheets appear shiny because a layer of non-corrosionable metal is fixed on the surface of corrosionable metal.
Collect information. (Text Book Page No. 108)
Question 1.
What are the various alloys used in daily life? Where are those used?
Answer:
| Various alloys | Uses |
| 1. Bronze | It is used to prepare: Coins, utensils, medals, statues |
| 2. Brass | Pipes, condenser tubes, utensils worshipping God. |
| 3. Stainless steel | Utensils, tools, dairy equipment, boilers. |
| 4. Steel | Construction of bridges and buildings, cutting tools, blades. |
| 5. Tungsten steel | High speed cutting tools |
| 6. Amalgam | Silver amalgam used by dentists |
| 7. Duralumin | Bodies of aircraft, buses, kitchenwares |
| 8. Aluminium bronze | Pigment in ink and paint |
| 9. German silver | Electrical heaters, resistors |
| 10. Gun metal | Guns, boiler fittings |
| 11. Magnelium | Beams of scientific balances, aircraft parts. |
| 12. Gold with copper or nickel or silver or platinum | Jewellery |
Question 2.
What are the properties that the alloy used for minting coins should have?
Answer:
The alloy used for minting coins should have excellent wear resistance and anti-corrosion properties.
Fill in the blanks:
Question 1.
……………has the highest melting point.
Answer:
Tungsten has the highest melting point.
Question 2.
Mercury and…………are two metals in the liquid state at room temperature.
Answer:
Mercury and galium are two metals in the liquid state at room temperature.
Question 3.
…………is the hardest natural substance.
Answer:
Diamond is the hardest natural substance.
Question 4.
The naturally occurring compounds of metals along with other impurities are known as………….
Answer:
The naturally occurring compounds of metals along with other impurities are known as minerals.
Question 5.
The minerals from which metals are extracted profitably and conveniently are called…………..
Answer:
The minerals from which metals are extracted profitably and conveniently are called ores.
Question 6.
An ore contains some of the impurities like soil, sand, etc. These impurities are called…………
Answer:
An ore contains some of the impurities like soil, sand, etc. These impurities are called gangue.
Question 7.
The process of extraction of a metal from its ore is called……….
Answer:
The process of extraction of a metal from its ore is called metallurgy.
Question 8.
Bauxite is a common ore of………..
Answer:
Bauxite is a common ore of aluminium.
Question 9.
…………. process is used for the purification of bauxite.
Answer:
Bayer’s process is used for the purification of bauxite.
Question 10.
During the electrolysis of alumina, ………..is liberated at the anode.
Answer:
During the electrolysis of alumina, oxygen is liberated at the anode.
Question 11.
The reaction of iron oxide with aluminium is known as…………..reaction.
Answer:
The reaction of iron oxide with aluminium is known as thermit reaction.
![]()
Question 12.
The process of coating a thin layer of zinc on iron is known as…………
Answer:
The process of coating a thin layer of zinc on iron is known as galvanising.
Question 13.
The metal that produces a sound on striking a hard surface is said to be………….
Answer:
The metal that produces a sound on striking a hard surface is said to be sonorous.
Question 14.
The process in which carbonate ores are changed into oxides by heating strongly in limited air is known as …………….
Answer:
The process in which carbonate ores are changed into oxides by heating strongly in limited air is known as calcination.
Question 15.
…………compounds are insoluble in solvents like kerosene and petrol.
Answer:
Ionic compounds are insoluble in solvents like kerosene and petrol.
Question 16.
…………… is used to obtain pure metals from impure metals.
Answer:
Electrolys is method is used to obtain pure metals from impure metals.
Question 17.
Corrosion can be prevented-by putting a layer of…………metal on corrosionable metal.
Answer:
Corrosion can be prevented by putting a layer of non-corrosionable metal on corrosionable metal.
Rewrite the following statements by selecting the correct options:
Question 1.
………… is a metal.
(a) Mg
(b) S
(c) P
(d) Br
Answer:
Mg is a metal.
Question 2.
………. is a nonmetal.
(a) Au
(b) Hg
(c) Br
(d) Cu
Answer:
Br is a nonmetal.
Question 3.
………… is a metalloid.
(a) Aluminium
(b) Antimony
(c) Zinc
(d) Mercury
Answer:
Antimony is a metalloid.
![]()
Question 4.
Metalloids have properties of ………..
(a) metals
(b) nonmetals
(c) both metals and nonmetals
(d) neither metals nor nonmetals
Answer:
Metalloids have properties of both metals and nonmetals.
Question 5.
…………. is a good conductor of electricity.
(a) Bromine
(b) Iodine
(c) Graphite
(d) Sulphur
Answer:
Graphite is a good conductor of electricity.
Question 6.
………. is a metal which is in liquid form at ordinary temperature and pressure.
(a) Magnesium
(b) Sodium
(c) Scandium
(d) Mercury
Answer:
Mercury is a metal which is in liquid form at ordinary temperature and pressure.
Question 7.
………. is an amphoteric oxide.
(a) Na2O
(b) MgO
(c) ZnO
(d) SO2
Answer:
ZnO is an amphoteric oxide.
Question 8.
……….. is an acidic oxide.
(a) Na2O
(b) CO2
(c) FeO3
(d) H2O
Answer:
CO2 is an acidic oxide.
Question 9.
………. is a basic oxide.
(a) CO2
(b) K2O
(C) SO2
(d) Al2O3
Answer:
K2O is a basic oxide.
Question 10.
………… is an ore of aluminium.
(a) Cryolite
(b) Bauxite
(c) Haematite
(d) Aluminium carbonate
Answer:
Bauxite is an ore of aluminium.
Question 11.
Bronze is an alloy of ………..
(a) copper and tin
(b) copper and zinc
(c) copper and iron
(d) iron and nickel
Answer:
Bronze is an alloy of copper and tin.
Question 12.
An alloy prepared from iron, nickel and chromium is known as …………
(a) brass
(b) bronze
(c) stainless steel
(d) amalgam
Answer:
An alloy prepared from iron, nickel and chromium is known as stainless steel.
Question 13.
…………. is an allotropic form of a nonmetal which conducts electricity.
(a) Sulphur
(b) Graphite
(c) Chlorine
(d) Iodine
Answer:
Graphite is an allotropic form of a nonmetal which conducts electricity.
Question 14.
………….. has an oxide which is soluble in sodium hydroxide.
(a) Calcium
(b) Magnesium
(c) Iron
(d) Zinc.
Answer:
Zinc has an oxide which is soluble in sodium hydroxide.
Question 15.
………… prevents the rusting of iron.
(a) Copper
(b) Zinc
(c) Aluminium
(d) Silver
Answer:
Zinc prevents the rusting of iron.
![]()
Question 16.
………….. is obtained by the reduction of its oxide by carbon.
(a) Zinc
(b) Aluminium
(c) Sodium
(d) Potassium
Answer:
Zinc is obtained by the reduction of its oxide by carbon.
Question 17.
………….. is used as an anode during the electrolytic reduction of bauxite.
(a) Sulphur
(b) Graphite
(c) Platinum
(d) Aluminium
Answer:
Graphite is used as an anode during the electrolytic reduction of bauxite.
Question 18.
Silver gets corroded due to ………… in air.
(a) oxygen
(b) hydrogen sulphide
(c) carbon dioxide
(d) nitrogen
Answer:
Silver gets corroded due to hydrogen sulphide in air.
Question 19.
…………. is the hardest substance and has the highest melting and boiling points.
(a) Iodine
(b) Sulphur
(c) Diamond
(d) Phosphorus
Answer:
Diamond is the hardest substance and has the highest melting and boiling points.
Question 20.
Jewellery articles are gold plated ………….
(a) to prevent corrosion
(b) to prevent rusting of the base metal
(c) to make articles attractive
(d) all of these
Answer:
(d) all of these
Question 21.
To show that zinc is more reactive than copper, the correct procedure is to ………..
(a) prepare copper sulphate solution and dip a zinc strip in it
(b) prepare zinc sulphate solution and dip a copper strip in it
(c) heat together zinc and copper strips
(d) add dil. nitric acid to both the strips
Answer:
To show that zinc is more reactive than copper, the correct procedure is to prepare copper sulphate solution and dip a zinc strip in it.
Question 22.
Iron is ………
(a) more reactive than zinc
(b) more reactive than aluminuium
(c) less reactive than copper
(d) less reactive than aluminium
Answer:
Iron is less reactive than aluminium.
Question 23.
A solution of Al2(SO4)3 in water is …………
(a) blue
(b) pink
(c) green
(d) colourless
Answer:
A solution of Al2(SO4)3 in water is colourless.
Question 24.
A solution of ………… in water is blue in colour.
(a) CuSO4
(b) FeSO4
(c) ZnSO4
(d) Al2(SO4)3
Answer:
A solution of CuSO4 in water is blue in colour.
Question 25.
A solution of …………. n water is green in colour.
(a) CuSO4
(b) FeSO4
(c) ZnSO4
(d) Al2(SO4)3
Answer:
A solution of FeSO4 in water is green in colour.
![]()
Question 26.
What would be the correct order if Zn, Fe, Al and Cu are arranged in increasing order of reactivity?
(a) Cu, Fe, Zn, Al
(b) Al, Cu, Fe, Zn
(c) Zn, Al, Cu, Fe
(d) Fe, Zn, Al, Cu (Practice Activity Sheet – 2)
Answer:
(a) Cu, Fe, Zn, Al
Question 27.
During the extraction of aluminium ……….
(a) Ingredients and gangue in bauxite
(b) Use of leaching during the concentration of ore
(c) Chemical reaction of transformation of bauxite into alumina by Hall’s process.
(d) Heating the aluminium ore with concentrated caustic soda.
Answer:
During the extraction of aluminium Chemical reaction of transformation of bauxite into alumina by Hall’s process.
Question 28.
A solution of CuSO4 in water is ………… in colour.
(a) pink
(b) blue
(c) colourless
(d) green
Answer:
A solution of CuSO4 in water is blue in colour.
Question 29.
Which of the following process is to be carried out to avoid the formation of greenish layer on brass vessels due to corrosion?
(a) Plating
(b) Anodization
(c) Tinning
(d) Alloying (Practice Activity Sheet – 3)
Answer:
(c) Tinning
State whether the following statements are True or False (If a statement is false, correct it and rewrite it.):
Question 1.
Metals are known as sonar metals.
Answer:
True.
Question 2.
Diamond is the softest natural substance.
Answer:
False. (Diamond is the hardest natural substance.)
Question 3.
Electrolysis method is used to obtain pure metals from impure metals.
Answer:
True.
Question 4.
Iodine and diamond are lustrous substances.
Answer:
True.
Question 5.
Aqua Regia is a mixture of conc. HCl and conc. HNO3 in the ratio of 1:3.
Answer:
False. (Aqua Regia is a mixture of conc. HCl and conc. HNO3 in the ratio of 3:1.)
Question 6.
Corrosion of metals can be stopped by detaching the air from metals.
Answer:
True.
Question 7.
Due to corrosion a greenish layer forms on the surface of copper or brass vessel.
Answer:
True.
Question 8.
Ionic compounds are soluble in kerosene.
Answer:
False. (Ionic compounds are soluble in water and insoluble in kerosene.)
Question 9.
Ionic compounds in the solid state conduct electricity.
Answer:
False. (Ionic compounds in the solid state do not conduct electricity.)
![]()
Question 10.
Mercury, silver and gold are very reactive metals.
Answer:
False. (Mercury, silver and gold are least reactive metals.)
Question 11.
In electroplating a metal is coated with another metal using electrolysis.
Answer:
True.
Question 12.
In anodising method. the copper or aluminium article is used as anode.
Answer:
True.
Question 13.
Silver plated spoon, gold plated ornaments are the examples of alloying.
Answer:
False. (Silver plated spoon, gold plated ornaments are the examples of electroplating)
Question 14.
silver amalgam is mainly used by dentists.
Answer:
True.
Question 15.
Aluminium oxide is an acidic oxide.
Answer:
False. (Aluminium oxide is an amphoteric oxide.)
Question 16.
copper reacts with moist carbon form copper carbonate.
Answer:
True.
Question 17.
Corrosion is degradation of a reaction with its environment.
Answer:
True.
Find the correlation in the given pair and rewrite the answer:
Question 1.
Brass : Copper and Zinc :: Bronze :………….
Answer:
Brass : Copper and Zinc :: Bronze : Copper and tin
Question 2.
Tinning : Tin :: Galvanizing :…………….
Answer:
Tinning : Tin :: Galvanizing : Zinc
Question 3.
Pressure cooker : Anodizing :: Silver plated spoons :…………..
Answer:
Pressure cooker : Anodizing :: Silver plated spoons : Electro-plating
Question 4.
The sulphides ores are strongly heated in air : Roasting :: The carbonates ores are strongly heated in a limited supply of air :………….
Answer:
The sulphides ores are strongly heated in air : Roasting :: The carbonates ores are strongly heated in a limited supply of air : Calcination.
Question 5.
Sulphide ores : Froth floatation method : Cassiterite ore :………..
Answer:
Sulphide ores : Froth floatation method : Cassiterite ore : Magnetic separation method.
Find the odd one out:
Question 1.
Sodium, Potassium, Silver, Sulphur
Answer:
Sulphur. (All except sulphur, others are metals.)
Question 2.
Boron, Chlorine, Bromine, Fluorine
Answer:
Boron. (All except boron, others are nonmetals.)
![]()
Question 3.
Copper, Iron, Mercury, Brass
Answer:
Brass. (All except brass, others are metals.)
Question 4.
Brass, Bronze, Phosphorus, Stainless steel
Answer:
Phosphorus. (All except phosphorus, others are alloys.)
Question 5.
Magnesium chloride, Sodium chloride, Water, Zinc chloride
Answer:
Water. (All except water, others are ionic compounds.)
Question 6.
Tinning, Anodization, Alloying, Froth floatation (March 2019)
Answer:
Froth floatation. (All except froth floatation, others are processes of coating a thin layer of metal on the surface of other metals.)
Match the following:
Question 1.
| Column I | Column II |
| (1) ZnS | (a) Cuprous sulphide |
| (2) HgS | (b) Bauxite |
| (3) Cu2S | (c) Zinc blend |
| (4) Al2O3.H2O | (d) Cinnabar |
| (e) Cryolite |
Answer:
(1) ZnS – Zinc blend
(2) HgS – Cinnabar
(3) Cu4S – Cuprous sulphide
(4) Al2O3.H2O – Bauxite.
Question 2.
| Column I | Column II |
| (1) Copper and zinc | (a) Stainless steel |
| (2) Copper and tin | (b) Zinc amalgam |
| (3) Iron, nickel and chromium | (c) Bronze |
| (4) Mercury and zinc | (d) Brass |
| (e) Steel |
Answer:
(1) Copper and zinc – Brass
(2) Copper and tin – Bronze
(3) Iron, nickel and chromium – Stainless steel
(4) Mercury and zinc – Zinc amalgam.
![]()
Question 3.
| Column I | Column II |
| (1) Galvanising | (a) Pressure cooker |
| (2) Tinning | (b) Silver plated spoons |
| (3) Electroplating | (c) Coating of tin on copper |
| (4) Anodizing | (d) Coating of Zn on iron |
Answer:
(1) Galvanising – Coating of Zn on iron
(2) Tinning – Coating of tin on copper
(3) Electroplating – Silver plated spoons
(4) Anodizing – Pressure cooker.
Translate the following statements into chemical equations and then balance them:
Question 1.
steam is passed over aluminium.
Answer:
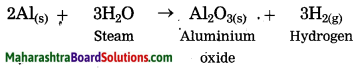
Question 2.
Extraction of copper from its sulphide ore.
Answer:
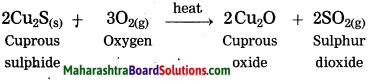
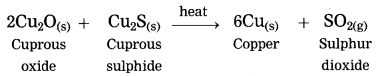
Question 3.
Thermit reaction.
Answer:

Question 4.
Magnesium reacts with hot water.
Answer:
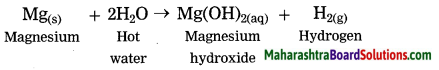
Question 5.
what happens when aluminium oxide dissolves in aqueous sodium hydroxide?
Answer:

Question 6.
Zinc reacts with sulphuric acid.
Answer:
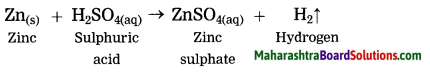
![]()
Question 7.
Iron reacts with sulphuric acid.
Answer:

Name the following:
Question 1.
A metal which forms an amphoteric oxide.
Answer:
Aluminium forms an amphoteric oxide.
Question 2.
An alloy of copper and zinc.
Answer:
An alloy of copper and zinc is termed as brass.
Question 3.
A compound which is added to lower the fusion temperature.
Answer:
Cryolite (AlF3, 3NaF) and fluorspar (CaF2) are added to lower the fusion temperature.
Question 4.
A metal which does not react with cold water but reacts with steam.
Answer:
Aluminium does not react With cold water but reacts with Steam.
Question 5.
A common ore of aluminium.
Answer:
Bauxite (Al2O3.H2O) is a common ore of aluminium.
Question 6.
A metal which is in liquid state at ordinary temperature.
Answer:
Mercury is in liquid state at ordinary temperature.
![]()
Question 7.
Two metals which are malleable.
Answer:
Iron and aluminium are malleable metals.
Question 8.
Two metals which are ductile.
Answer:
Gold and silver are ductile metals.
Question 9.
Two metals which are good conductors of heat.
Answer:
Silver and copper are good conductors of heat.
Question 10.
Two metals which are good conductors of electricity.
Answer:
Copper and aluminium are good conductors of electricity.
Question 11.
Two metals which are used for making cooking vessels.
Answer:
Copper and aluminium are used in making cooking vessels.
Question 12.
Two metals having low melting points.
Answer:
Sodium and potassium have low melting points.
Question 13.
Two highly reactive metals.
Answer:
Sodium and potassium are highly reactive metals.
Question 14.
A nonmetal which is in liquid state at room temperature.
Answer:
Bromine is in liquid state at room temperature.
Question 15.
Two ionic compounds.
Answer:
Sodium chloride (NaCl) and magnesium chloride (MgCl2) are ionic compounds.
Question 16.
The process of heating the sulphide ore to a high temperature in the excess of air.
Answer:
In roasting, sulphide ore is heated to a high temperature in the excess of air.
Question 17.
The process of heating the carbonate ore to a high temperature in limited air.
Answer:
In calcination, carbonated ore is heated to a high temperature in limited air.
![]()
Question 18.
The compound formed by the reaction between aluminium oxide and sodium hydroxide.
Answer:
Sodium aluminate is formed by the reaction between aluminium oxide and sodium hydroxide.
Question 19.
Two metals which are found in the free state in nature.
Answer:
Gold (Au) and silver (Ag) are found in the free state in nature.
Question 20.
A metal which has the highest melting point.
Answer:
Tungsten has the highest melting point.
Question 21.
Two nonmetals which are lustrous.
Answer:
Iodine and diamond are lustrous in nature.
Answer the following questions in one sentence each:
Question 1.
State the property of the metals due to which they can be drawn into wires.
Answer:
The property of the metal due to which they can be drawn into wires is called ductility.
Question 2.
State the property of the metals due to which they can be beaten into thin sheets.
Answer:
The property of the metals due to which they can be beaten into thin sheets is called malleability.
Question 3.
Which is the hardest substance?
Answer:
Diamond which is a form of carbon is the hardest substance.
Question 4.
What material is used to coat electrical wires?
Answer:
PVC (Polyvinyl chloride) is used to coat electrical wires.
Question 5.
State two metals which can be cut easily with a knife.
Answer:
Sodium and potassium are soft metals and can be cut easily with a knife.
Question 6.
Which of the following metals react with cold water?
Sodium, iron, copper, potassium.
Answer:
Sodium and potassium metals react with cold water.
Question 7.
Which of the following metals do not react with cold water or hot water?
Sodium, potassium, aluminium, iron.
Answer:
Aluminium and iron do not react with cold water or hot water.
Question 8.
State two metals which displace hydrogen from dilute acids and two metals which do not do so.
Answer:
Metals which displace hydrogen from dilute acids are: Magnesium and zinc.
Metals which do not displace hydrogen from dilute acids are: Copper and silver.
![]()
Question 9.
Arrange the following metals in the increasing order of their activity:
Copper, Silver, Aluminium, Iron. (Practice Activity Sheet – 1)
Answer:
The arrangement of metals in the increasing order of their activity:
Silver < Copper < Iron < Aluminium
Question 10.
Write the chemical equation for the reaction of hot iron with steam.
Answer:

Question 11.
Complete the following reactions:
(1) Zn(s) + H2O(g) → _____________
![]()
Answer:
(1) Zn(s) + H2O(g) → ZnO(s) + H2(g)
![]()
Question 12.
Complete the following reactions:

Answer:

Question 13.
3MnO2 + 4Al → 3Mn + 2Al2O3 + heat.
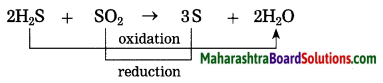
Identify the substances undergone oxidation and reduction reactions.
Answer:
MnO2 is reduced to Mn.
Al is oxidised to Al2O3
![]()
Question 14.
State the impurities present in the bauxite ore.
Answer:
The main impurities present in the bauxite ore are silica (SiO2) and iron oxide (Fe2O3).
Question 15.
Write the formula of (i) bauxite (ii) cryolite.
Answer:
The formula of bauxite is Al2O3·H2O and that of cryolite is (Na3AlF6).
Question 16.
What is galvanization?
Answer:
The process of coating a thin layer of zinc on iron or steel is called galvanization.
Question 17.
Name the reaction in which aluminium is used as a reducing agent.
Answer:
The thermite reaction in which iron oxide is reduced by aluminium. Aluminium is used as a reducing agent in the thermit reaction.
Question 18.
What are the constituents of bronze?
Answer:
Copper and tin are the constituents of bronze.
Question 19.
State the term used to express the purity of gold.
Answer:
The purity of gold is expressed in carat.
Question 20.
What is meant by amalgam?
Answer:
The amalgam is an alloy in which one of the metals is mercury.
Question 21.
What is meant by electroplating?
Answer:
A process in which a less reactive metal is coated on a more reactive metal by electrolysis is called electroplating.
Question 22.
Why are metals called electropositive elements?
Answer:
Metals are reactive. They lose electrons and become positively charged ions. Therefore, metals are called electropositive elements.
Answer the following questions:
Question 1.
Distinguish between the physical properties of metals and nonmetals with respect to the following points:
(1) Physical state (2) Lustre (3) Ductility and malleability (4) Conduction of heat and electricity (5) Hardness (6) Melting and boiling points.
Answer:
(1) Physical state: Under ordinary conditions, metals are generally solids. Exceptions: mercury and gallium are liquids. Under ordinary conditions, nonmetals may be solids or gases. Exception: bromine is in liquid state.
(2) Lustre: Metals usually have a high lustre (called metallic lustre). They can be polished to give a highly reflective surface. With the exceptions of gold and copper, metals usually have silvery grey colour. Nonmetals lack lustre, exceptions: graphite and iodine. Some nonmetals are colourless and others possess a variety of colours.
(3) Ductility and malleability: Metals are ductile and malleable. Nonmetals are not ductile and mallfeable.
(4) Conduction of heat and electricity: Metals are good conductors of heat and electricity. Nonmetals are bad conductors of heat and electricity. Exception: Graphite is a good conductor of electricity.
(5) Hardness: Metals are usually hard, but not brittle, exceptions: sodium, potassium, lead, zinc. Nonmetals are brittle in the solid state, exception: diamond.
(6) Melting and boiling points: The melting and boiling points of metals are high, exceptions: sodium, potassium, mercury, gallium. The melting and boiling points of nonmetals are low, exceptions: carbon, silicon.
![]()
Question 2.
Write any three physical properties of nonmetals.
Answer:
- Nonmetals may be solid or gaseous.
- Nonmetals lack lustre. They are not ductile and malleable.
- The melting and boiling points of nonmetals are low.
- Nonmetals are bad conductors of heat and electricity.
Question 3.
Metals are good conductors of heat. Explain why.
Answer:
(1) The electrons in the outermost shells of atoms of a metal are free to move throughout the metal.
(2) When a metal is heated, these electrons start moving with higher velocity and conduct heat. Hence, metals are good conductors of heat.
Question 4.
Metals are good conductors of electricity. Explain why.
Answer:
(1) The electrons in the outermost shells of atoms of a metal are free to move throughout the metal.
(2) When a potential difference is applied between the ends of a metal wire, the net movement of the electrons in a particular direction, from a point at lower potential to a point at higher potential, constitutes an electric current. Hence, metals are good conductors of electricity.
Question 5.
A metal can be drawn into a wire. Explain why.
Answer:
- The property due to which a substance can be drawn into a thin wire without cracking or breaking is called ductility.
- Metals are ductile. Thus, a metal can be drawn into a wire.
Question 6.
A metal can be hammered into a thin sheet. Explain why.
Answer:
- The property due to which a substance can be hammered (or rolled) into a thin sheet without cracking is called malleability.
- Metals are malleable. Thus, a metal can be hammered to form a thin sheet.
Question 7.
How do metals react with oxygen?
Answer:
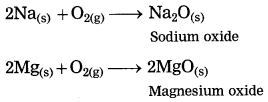
Metals combine with oxygen on heating in air and metal oxides are formed.
Metal + Oxygen → Metal oxide
Question 8.
How does a metal react with water?
Answer:
Sodium and potassium react vigorously with water to evolve hydrogen. Calcium reacts with water slowly and less vigorously to evolve hydrogen and the metal floats on water. Magnesium reacts with hot water to evolve hydrogen. Aluminium, iron and zinc do not react with cold or hot water but they react with steam to evolve their oxides and hydrogen.
2Na(s) + 2H2O(l) → 2NaOH(aq) + H2(g) + heat energy
2K(s) + 2H2O(l) → 2KOH(aq) + H2(g) + heat energy
2Ca(s) + 2H2O(l) → 2Ca(OH)2(aq) + H2(g)
Mg(s) + 2H2O(hot) → Mg(OH)2(aq) + H2(g)
2Al(s) + 3H2O steam → Al2O3(s) + 3H2(g)
3Fe(s) + 4H2O steam → Fe3O4 + 4H2(g)
Zn(s) + H2O steam → ZnO(s) + H2(g)
![]()
Question 9.
(9) How does a metal react with an acid?
Answer:
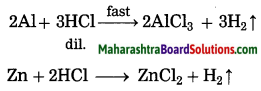
Reaction of metals with acids: Metals react with dilute hydrochloric acid or dilute sulphuric acid to form metal chloride or metal sulphate and hydrogen gas. The rate of evolution of H2 is maximum in case of magnesium. The reactivity decreases in the order
Mg > Al > Zn > Fe.
Mg(s) + 2HCl(aq) → MgCl2(s) + H2(g)
2Al(s) + 6HCl(aq) → 2AlCl3(aq) + 3H2(g)
Zn(s) + 2HCl(aq) → ZnCl2(aq) + H2(g)
Fe(s) + 2HCl(aq) → FeCl2(aq) + H2(g)
Fe(s) + H2SO4(aq) → FeSO4 + H2(g)
Zn(s) + H2SO4(aq) → ZnSO4 + H2(g)
Mg(s) + H2SO4(aq) → MgSO4(aq) + H2(g)
Question 10.
How does a metal react with nitric acid?
Answer:
Metals react with nitric acid to form nitrate salts. Depending on the concentration of nitric acid, various oxides of nitrogen (NO, NO2) are formed.
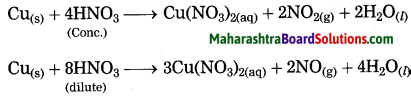
Question 11.
Arrange the following metals in the decreasing order of chemical reactivity:
Cu, Mg, Fe, Ca, Zn, Na.
Answer:
The reactivity of metal decreases in the following order:
Na > Mg > Ca > Zn > Fe > Cu.
Question 12.
What is meant by aqua regia?
Answer:
Aqua regia is a highly corrosive and fuming liquid. It is a freshly prepared mixture of conc. HCl and conc. HNO3 in the ratio of 3:1. Most of the substances dissolve in it. Aqua regia is a reagent which dissolves gold and platinum.
Question 13.
How does a metal react with salts of other metals?
Answer:
The reaction of metals with solutions of salts of other metals is the displacement reaction. If a metal A displaces other metal B from the solution of its salt, it means that the metal A is more reactive than the metal B.
Metal A + Salt solution of metal B → Salt solution of metal A + metal B
![]()
In this reaction Fe has displaced Cu from CuSO4. It means Fe is more reactive than Cu.
Question 14.
Explain the reactivity series of the metals.
Answer:
The arrangement of metals in decreasing order of their reactivity in the form of a series is called the reactivity or activity series of the metals.
The most reactive metal is placed at the top of the list and least reactive metal is placed at the bottom of the list.
On the basis of reactivity, we can classify metals into the following categories:
- High reactivity metals
- Moderately reactive metals
- Less reactive metals.
1. Extraction of High reactivity metals: The metals which are placed at the top of the reactivity series are very reactive. They are never found in nature as free elements, e.g., sodium, potassium, calcium and aluminium. These metals are obtained by electrolytic reduction.
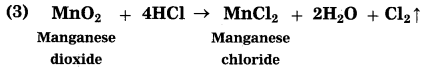
2. Extraction of Moderately reactive metals: The metals in the middle of reactivity series such as iron, zinc, lead, copper are moderately reactive. These elements are present as sulphides or carbonates in nature. Generally metals are obtained from their oxide as compared to their sulphides and carbonates.
3. Extraction of Less reactive metals: The metals which are placed at the bottom of the reactivity series are least reactive. They occur in free state, e.g. gold, silver and copper. Copper and silver are also found in the combined state as sulphide and oxide ores. These metals are obtained from their ores by just heating the ores in air.
![]()
Question 15.
Atomic number of metal “A” is 11, while atomic number of metal “B” is 20. Which of them will be more reactive? Write the chemical reaction of dilute HCl with metal “A”. (Practice Activity Sheet – 2)
Answer:
Metal ‘A’ is more reactive than metal ‘B’.
Atomic number of metal ‘A’ is 11, hence it is Na.
2Na + 2HCl → 2NaCl(aq) + H2(g)
Question 16.
How does a metal react with a nonmetal?
Answer:
By oxidation of a metal, cations are formed, on the other hand by reduction of a nonmetal, anions are formed. The ionic compound is formed due to the metal losing electrons while the nonmetal accepts the electrons. The ionic compound of sodium chloride is formed as sodium loses one electron while chlorine accepts one electron.
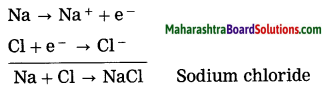
Similarly Mg and K form ionic compounds MgCl2 and KCl.
Question 17.
How do nonmetals react with oxygen?
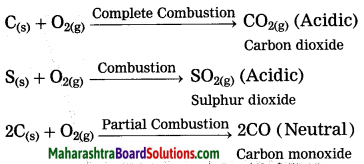
Answer:
Nonmetals combine with oxygen to form acidic oxides. In some cases, neutral oxides are formed.
Question 18.
How do nonmetals react with water?
Answer:
Nonmetals do not react with water, (exception : halogen). Chlorine dissolves in water giving hypochlorous acid.

Question 19.
How do nonmetals react with dilute acids?
Answer:
Nonmetals do not react with dilute acid, (exception: halogen). Chlorine reacts with dil. hydrobromic acid to form bromine and HCl.

Question 20.
How do nonmetals react with hydrogen?
Answer:
Nonmetals react with hydrogen under certain conditions (such as proper temperature, pressure, catalyst, etc.)
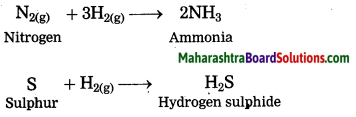
Question 21.
What is meant by an ionic compound?
Answer:
The compound formed from two units, namely cation and anion is called an ionic compound.
Question 22.
What is meant by an ionic bond?
Answer:
The cation and anion being oppositely charged, there is an electrostatic force of attraction between them, this force of attraction between cation and anion is called the ionic bond.
![]()
Question 23.
State the general properties of ionic compounds.
Answer:
- Ionic compounds are solids and hard due to strong electrostatic force of attraction between oppositely charged ions.
- They are generally brittle. When pressure is applied they break into pieces.
- They have high melting and boiling points, due to intermolecular force of attraction is high in ionic compounds.
- They are soluble in water and insoluble in solvents such as kerosene and petrol.
- Ionic compounds cannot conduct electricity when in solid state, they are electrically neutral. They conduct electricity in the molten state and also in an aqueous solution.
Question 24.
Explain the following terms:
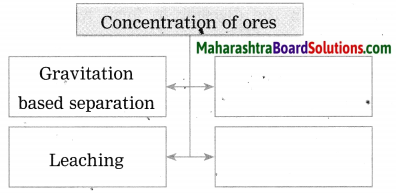
1. Concentration of ores
2. Roasting
3. Calcination
4. Refining
Answer:
1. Concentration of ores: The process of separating gangue from the other ores is called concentration of ores.
2. Roasting: The process of heating an ore to a high temperature in excess of air and converting it into its oxide is called roasting.
Examples: ZnS (zinc blend), PbS (Galena)
![]()
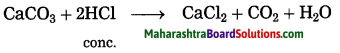
3. Calcination: The process of heating an ore in a limited supply of air and converting it into its oxide is called calcination.
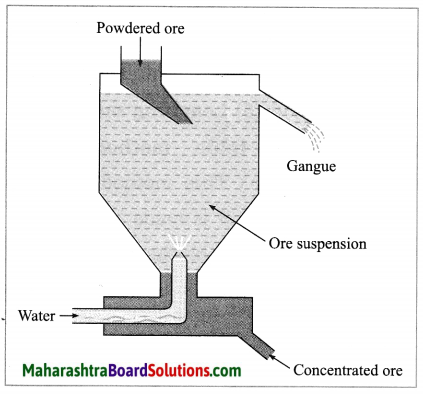
Example: Zinc carbonate (ZnCO3)
ZnCO3 → ZnO + CO2 ↑
4. Refining: The metal obtained by chemical reduction contains impurities. The process of electrolysis method is used to obtain pure metals from impure metals is known as refining.
Question 25.
State two methods of concentration of ores in which the heavy particles of ores can be separated from the light gangue particles by the gravitational method.
Answer:
- Wilfley table method
- Hydraulic separation method are two methods of concentration of ores in which the heavy particles of ores can be separated from the light, gangue particles by the gravitational method.
Question 26.
What are the different methods used for removing gangue from ores?
(OR)
Write the five methods of concentration of ores.
Answer:
- Wilfley table method
- Hydraulic separation method
- Magnetic separation method
- Froth floatation method
- Leaching method.
Question 27.
Write short notes on: (1) Wilfley table method (2) Hydraulic separation method (3) Magnetic separation method (4) Froth floatation method (5) Leaching method.
Answer:
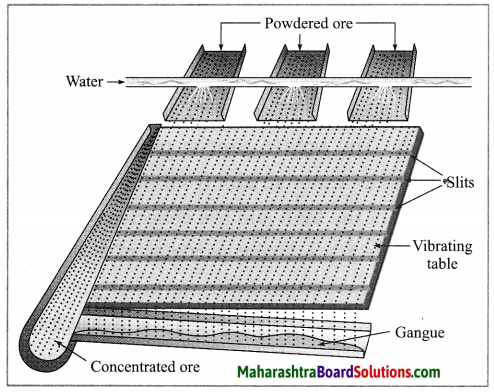
(1) Wilfley table method : (Separation based on gravitation) This method of separation uses the Wilfley table, it is made by fixing narrow and thin wooden wedges/blocks on inclined surface with low slope. The table is kept continuously vibrating.
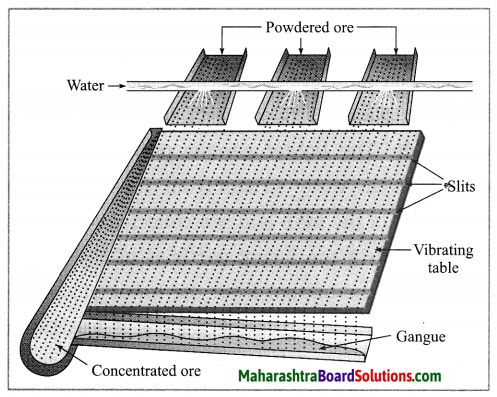
Lumps of the ore is made powdered ore by using ball mill. This powdered ore is poured on the table and a stream of water is simultaneously released from the upper side. This result in the lighter gangue particles getting carried away along with the flowing water, while the heavier particles in which proportion of minerals is more and proportion of gangue particles is less, are blocked by the wooden wedges and is collected through the slits between them.
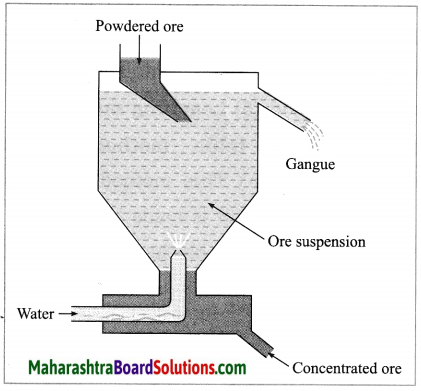
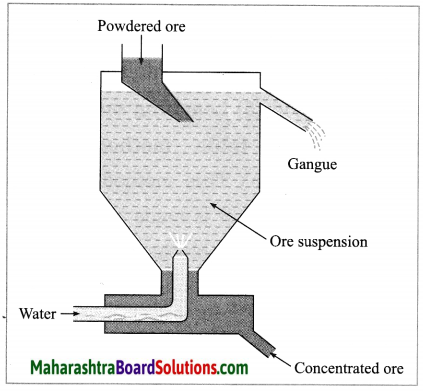
(2) Hydraulic separation method: The hydraulic separation method is based on the working of a mill. This is a tapering vessel similar to that used in a grinding mill. It opens in a tank like a container that is tapering on the lower side. The tank has an outlet for water on the upper side and a water inlet on the lower side.
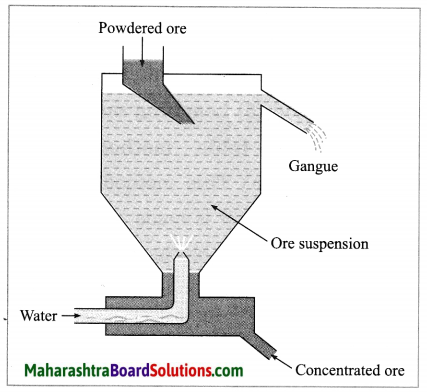
Finely ground ore is added to the tank. A fast stream of water is released in the tank from the lower side. The lighter gangue particles flow out along with the water stream from the outlet on the upper side of the tank and are collected separately, simultaneously the heavy particles of the ore are collected at the bottom from the lower side of the tank. This method is based on the law of gravitation, wherein particles of the same size are separated by their weight with the help of water.
(3) Magnetic separation method: Electro-magnetic machine is used in this method. The main parts of this machine are two types of iron rollers and the conveyor belt continuously moving around them. One of the rollers is nonmagnetic while the other is electromagnetic. The conveyor belt moving around the rollers is made up of leather or brass (nonmagnetic). The powdered ore is poured at that end of the conveyor belt which is on the side of the nonmagnetic roller. Two collector vessels are placed below the magnetic roller.
The particles of the nonmagnetic part in the ore are not attracted towards the magnetic roller. Therefore, they are carried out further along the belt and fall in the collector vessel which is away from the magnetic roller. Simultaneously the particles of the magnetic ingredients of the ore stick to the magnetic roller and therefore fall in the collector vessel near the belt.
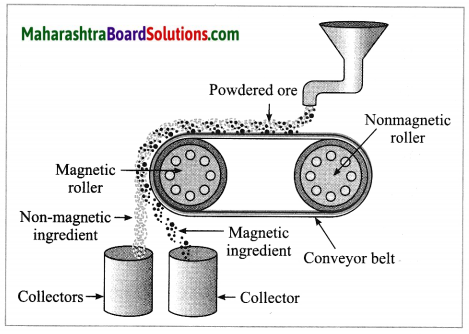
In this way the magnetic and nonmagnetic particles in the ore are separated because of their magnetic nature. For example, cassiterite is a tin ore. It contains mainly the nonmagnetic ingredient stannic oxide (SnO2) and the magnetic ingredient ferrous tungstate (FeWO4). These are separated by the electromagnetic method.
(4) Froth floatation method: The froth floatation method is based on the two opposite properties, hydrophilic and hydrophobic, of the particles. The metal sulphides particles get wet mainly with oil due to their hydrophobic property. The gangue particles get wet with water due to the hydrophilic property.
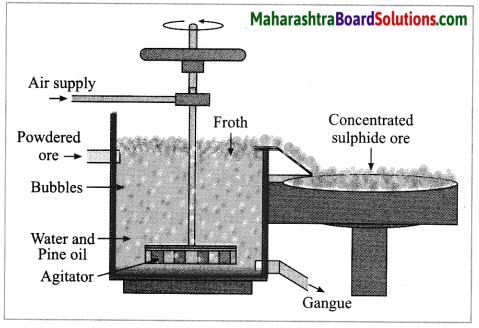
In this method the finely ground mineral is put into a big tank containing a lot of water. The finely powdered ore and vegetable oil such as pine oil, eucalyptus oil are mixed with water for formation of froth. The pressurised air is blown through the mixture. There is an agitator rotating around its axis in the centre of the floatation tank. The agitator is used as per the requirement. Bubbles are formed due to the blown air.
A foam is formed from oil, water and air bubbles together, due to the agitating. This foam rises to the surface of the water and floats. Hence this method is called froth floatation. Sulphide minerals float with the foam on water as they get and can be removed. The gangue particles are wetted by water, settles down at the bottom. This method is used for concentration of zinc blend (ZnS) and copper pyrite (CuFeS2).
(5) Leaching: Leaching is the first step in the extraction of the metals like aluminium, gold and silver from their ores. In this method the ore is soaked in a particular solution for long time. The ore dissolves in that solution due to specific chemical reaction. The gangue, however, does not react and therefore does not dissolve in that solution. It can be separated easily.
For example, concentration of bauxite, the aluminium ore, is done by leaching method. Bauxite is soaked in aqueous NaOH or aqueous Na2CO3 which dissolves the main ingredient alumina in it. This means that bauxite is leached by sodium hydroxide.
![]()
Question 28.
Draw a neat labelled diagram of the arrangement of the equipment used in (1) Wilfley table method (2) Hydraulic separation method.
Answer:
1. Wilfley table method:
2. Hydraulic separation method:
Question 29.
Complete the following flow chart and answer the questions below:
(i) In which method pine oil is used?
(ii) Explain that method of concentration in brief. (Practice Activity Sheet – 2)
Answer:
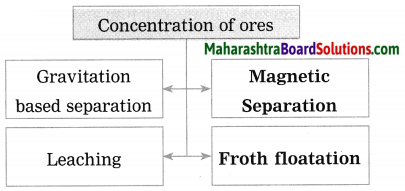
(i) Pine oil is used in froth floatation method.
(ii) The finely powdered ore and vegetable oil such as pine oil, eucalyptus oil are mixed with water for formation of froth. The pressurised air is blown through the mixture. The agitator is used as per the requirement. Bubbles are formed due to the blown air. A foam is formed from oil, water and air bubbles together, due to the agitating. This foam rises to the surface of the water and floats. Hence this method is called froth floatation. Sulphide minerals float with the foam on water as they get and can be removed. The gangue particles are wetted by water, settles down at the bottom. This method is used for concentration of zinc blend (ZnS) and copper pyrite (CuFeS2).
Question 30.
A tapping vessel opens in a tank like container that is tapering on the lower side. The tank has an outlet for water on the upper side and a water inlet on the lower side. Finely ground ore is released in the tank. A forceful jet of water is introduced in the tank from lower side and gangue particles and pure ore are separated by this method.
(i) The above description is of which gravitation separation method?
(ii) Draw labelled diagram of this method. (March 2019)
Answer:
(i) Hydraulic separation method.
(ii)
Question 31.
How are sodium, magnesium and potassium obtained from their molten chloride salts?
Answer:
The metals sodium, calcium and magnesium are obtained by electrolysis of their molten chloride salts. In this process metal is deposited on the cathode while chlorine gas is liberated at the anode.
Question 32.
Name the main ore of aluminium.
Answer:
Bauxite (Al2O3·H2O) is the main ore of aluminium.
![]()
Question 33.
What is bauxite? What are the main impurities found in this ore?
Answer:
Bauxite (Al2O3·H2O) is hydrated aluminium oxide. It contains 30% to 70% Al2O3. The main impurities present in it are iron oxide (Fe2O3) and sand (SiO2).
Question 34.
From which ore is aluminium extracted? What are the stages in its extraction (give only names)?
Answer:
Aluminium is extracted from bauxite (Al2O3·nH2O). Stages id the extraction: (i) Concentration of ore, i.e., conversion of bauxite into alumina, (ii) Electrolytic reduction of alumina.
Question 35.
Describe Bayer’s process for concentration of bauxite.
Answer:
(1) Bayer’s process is used to obtain pure aluminium oxide from bauxite.
(2) Bauxite is then concentrated by chemical separation. Bauxite contains impurities like iron oxide (Fe2O3) and silica (SiO2).
(3) Bauxite ore is powdered and heated with sodium hydroxide under high pressure for 2 to 8 hours at 140 °C in the digester. The aluminium oxide being amphoteric in nature present in bauxite reacts with sodium hydroxide to form water soluble sodium aluminate. This means that bauxite leached by sodium hydroxide. Silica reacts with sodium hydroxide to form soluble sodium silicate. The basic iron oxide (Fe2O3) in the gangue remains unaffected. It is separated by filtration.
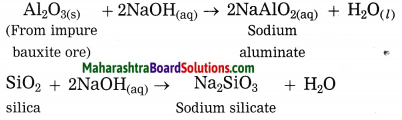
(4) The filtrate containing sodium aluminate and sodium silicate is stirred with water and then cooling to 50° C. It is hydrolysed to give precipitate of aluminium hydroxide.

(5) Aluminium hydroxide is then filtered, washed with water, dried and then calcinated by heating at 1000 °C to get pure aluminium oxide.
![]()
Question 36.
Describe Hall’s process for concentration of bauxite.
Answer:
In Hall’s process the ore is powdered and then it is leached by heating with aqueous sodium carbonate in the digester to form water soluble sodium aluminate. Then the insoluble impurities are filtered opt. The filtrate is warmed and neutralised by passing carbon dioxide gas through it. This result in precipitation of aluminium hydroxide.
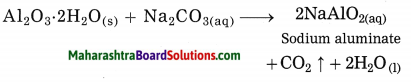

The precipitate of Al(OH)3 obtained in this processes is filtered, washed, dried and then calcinated by heating at 1000 °C to obtain alumina.
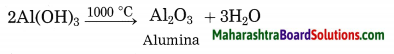
Question 37.
Describe the process of preparation of aluminium by the electrolysis of alumina.
(OR)
Draw and label the diagram of electrolysis of alumina and explain the electrolytic reduction of alumina.
Answer:
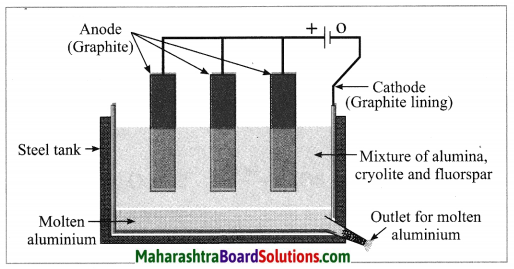
Electrolytic reduction of alumina:
(1) The electrolytic cell consists of a rectangular steel tank lined from inside with graphite.
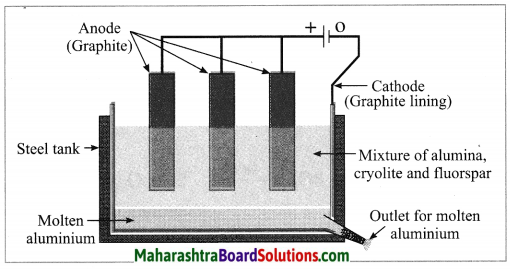
(2) The carbon lining (graphite) acts as a cathode. The anode consists of graphite rods suspended in the molten electrolyte.
(3) Alumina has very high melting point ( > 2000 °C). The electrolysis of alumina is carried out at a low temperature by dissolving it in molten cryolite (Na3AlF6). The solution of alumina in cryolite and small amount of fluorspar (CaF2) is added in the mixture to lower its melting point up to 1000 °C.
(4) On passing an electric current, alumina is electrolysed.
(5) Molten aluminium is collected at the cathode, while oxygen gas is evolved at the anode.
The electrode reactions are shown below:
Al2O3 → 2Al3+ + 3O2-
Anode reaction: 2O2- → O2(g) + 4e–
Cathode reaction: Al3+ + 3e– → Al
The molten aluminium is heavier than the electrolyte. Therefore, it sinks to the bottom of the electrolyte and is removed from time to time. About 99% pure aluminium is obtained by this process. The oxygen gas liberated reacts with carbon anode and forms carbon dioxide. As the anode gets oxidised during the electrolysis of alumina, it has to be replaced from time to time.
![]()
Question 38.
In the extraction of aluminium:
(i) Name the process of concentration of bauxite.
Answer:
The process of concentration of bauxite is known as Bayer’s process.
(ii) Write the cathode reaction in electrolytic reduction of alumina.
Answer:
At the cathode: Al3+ + 3e– → Al.
(iii) Write the function and formula of cryolite in the extraction of aluminium.
Answer:
Cryolite is added to the molten mixture of alumina to reduce the melting point to about 1000 °C.
The formula of cryolite is (Na3AlF6) or AlF3, 3NaF.
(iv) write an equation for the action of heat on aluminium hydroxide.
Answer:

(v) Draw the diagram of extraction of aluminium.
Answer:
(vi) Write the anode reaction in electrolytic reduction of alumina.
Answer:
Al2O3 → 2Al3+ + 3O2-
At Anode: 2O2- → O2(g) + 4e–
(vii) Write the cathode reaction in electrolytic reduction of alumina.
Answer:
Al2O3 → 2Al3+ + 3O2-
Cathode: Al3+ + 3e– → Al(l)
Question 39.
What happens when aluminium ore is heated with caustic soda? Write the balanced chemical equation for the same.
Answer:
When aluminium ore is heated with caustic soda solution under high pressure for 2 to 8 hours and at 140 °C to 150 °C, aluminium oxide from aluminium ore, being amphoteric in nature, dissolves in caustic soda solution to form sodium aluminate.
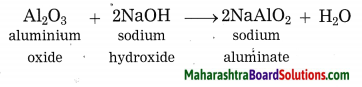
Question 40.
How is zinc extracted from its ore zinc sulphide or zinc carbonate?
Answer:
The crude zinc sulphide ore is heated strongly in excess of air. Zinc sulphide is converted into zinc oxide. This process is known as roasting.
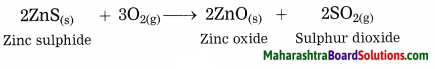
(OR)
The crude zinc carbonate ore is heated strongly in limited supply of air. Zinc carbonate is converted into zinc oxide. This process is known as calcination.
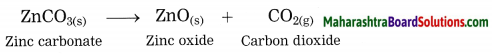
The zinc oxide is reduced to zinc by using a reducing agent such as carbon.
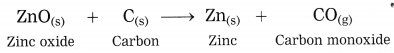
Question 41.
How is copper extracted from its sulphide ore?
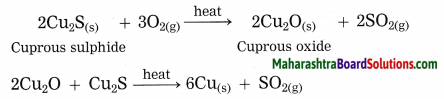
Answer:
Copper is found as cuprous sulphide (Cu2S) in nature. When Cu2S is heated in air, copper is obtained.
Question 42.
How is mercury extracted from cinnabar?
(OR)
Extraction of mercury from its ore cinnabar and write the corresponding chemical reaction.
Answer:
Cinnabar is an ore of mercury. When cinnabar is heated (roasted), it is converted into mercuric oxide (HgO). Mercuric oxide is then reduced to mercury on further heating.
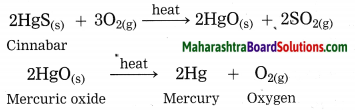
Question 43.
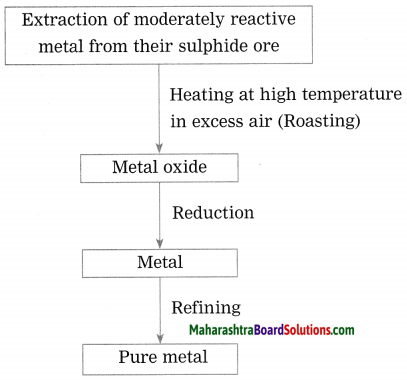
Show the steps involved in the extraction of moderately reactive metals from their sulphide ores.
Answer:
Moderately reactive elements are present as sulphides or carbonates in nature.
Question 44.
In the reactivity series of metals, some metals are misplaced. Rearrange these metals in the decreasing order of their reactivity.

Answer:

![]()
Question 45.
Complete the table, if a metal reacts with the reagent then mark ✓ and if not then ✗.
| Metal | Ferrous sulphate |
Silver nitrate |
Copper sulphate |
Zinc sulphate |
| Cu | ||||
| Al |
Answer:
| Metal | Ferrous sulphate |
Silver nitrate |
Copper sulphate |
Zinc sulphate |
| Cu | ✗ | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ |
| Al | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
Question 46.
Explain the term corrosion with a suitable example.
(OR)
What is corrosion ?
Answer:
The process in which a metal is destroyed gradually by the action of air, moisture or a chemical (like an acid) on its surface is called corrosion.
(OR)
Corrosion is degradation of a material due to reaction with its environment.
The major problem of corrosion occurs with iron, as it is used as a structural material in construction, bridges, shipbuilding.
Iron gets covered by reddish brown flakes when exposed to atmosphere. This is an example of corrosion.
Question 47.
Explain the different methods to prevent corrosion of metals.
Answer:
(1) Corrosion of a metal can be prevented if the contact between metal and air is cut off.
(2) Corrosion of a metal is prevented by coating with something which does not allow moisture and oxygen to react with it.
(3) A layer of oil or paint or grease is applied on the surface of a metal to prevent corrosion. The rusting or corrosion of iron can be prevented by this method.
(4) Corrosion is also prevented by coating a corrosive metal with a noncorrosive metal. Galvanising, tinning, electroplating, anodising and alloying are the different methods in which a metal is coated with a noncorrosive metal to prevent corrosion.
Question 48.
Write three methods of preventing rusting of iron.
Answer:
- The rusting of iron can be prevented by painting, oiling, greasing or varnishing its surface.
- Galvanisation is another method of protecting iron from rusting by coating iron with a thin layer of zinc.
- Corrosion of iron is prevented by coating iron with noncorrosive substance like carbon. This process is termed as alloying.
Question 49.
What is meant by an alloy? Give two examples with chemical composition.
Answer:
The homogeneous mixture formed by mixing a metal with other metals or nonmetals in certain proportion is called an alloy.
Examples:
1. Bronze: Bronze is an alloy formed from 90% copper and 10% tin. Bronze statues stay well in sun and rain.
2. Stainless steel: Stainless steel alloy is made from 74% iron, 18% chromium and 8% carbon. This alloy does not get stained with air or water and does not rust.
Write short notes on the following:
Question 1.
Galvanizing.
Answer:
(1) The process of coating a thin layer of zinc on iron or steel is called galvanization.
(2) In this method corrosion of zinc occurs first because zinc is more electropositive than iron. After a few years zinc layer goes away and the iron layer gets exposed and starts rusting.
(3) In galvanization an iron object is dipped into molten zinc. A thin layer of zinc is formed all over the iron object. Examples: Shiny iron nails, pin, iron pipes.
Question 2.
Tinning.
Answer:
The process of coating a thin layer of tin (molten tin) on copper or brass is called tinning. Cooking vessels made of copper and brass get a greenish coating due to corrosion. The greenish substance is copper carbonate and it is poisonous. If buttermilk or curry is placed in such a vessel it gets spoiled. Therefore, these vessels are coated with tin to prevent corrosion.
![]()
Question 3.
Electroplating.
Answer:
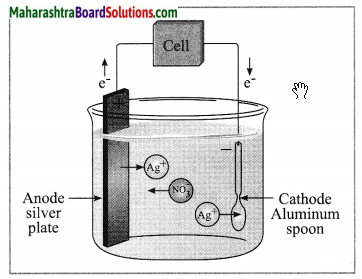
The process in which a less reactive metal is coated on a more reactive metal by electrolysis is called electroplating.
Examples: Silver-plated spoon, gold-plated jewellery.
(1) Which process will you study with the help of above material and solutions.
Answer:
With the help of above material and solutions, electroplating process is studied.
(2) Define the process.
Answer:
The process in which less reactive metal is coated on a more reactive metals by electrolysis is called electroplating.
(3) Write the anode and cathode reactions.
Answer:
At anode: Ag → Ag+ + e–
At cathode: Ag+ + e– → Ag
Question 4.
Anodizing.
(OR)
Identify the process shown in the above diagram and explain it in brief. (Practice Activity Sheet – 3)
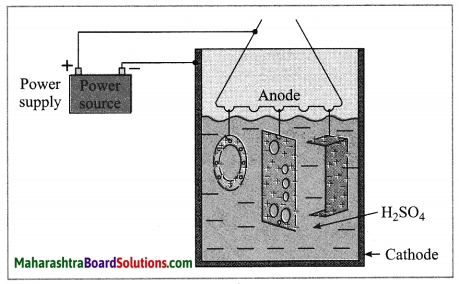
Answer:
The anodizing technique is an application of electrolysis. In this method copper or aluminium article is used as anode and it is coated with a strong film of their oxides by means of electrolysis. This oxide layer is strong and uniform all over the surface. This thin film protects the metals from corrosion. The protection can be further increased by making the oxide layer thicker during the anodization.
Examples: Kitchen articles such as ; anodized pressure cooker and anodized pan.
Question 5.
Alloying.
Answer:
A homogenous mixture of two or more metals or a metal and a nonmetal in a definite proportion is called an alloy. The physical properties of an alloy are different from those of its constituents. Alloys are corrosion resistant. Alloy decreases the intensity of corrosion of metals.
Examples: Brass is made from copper and zinc, 90 % Copper and 10 % tin are used to make an alloy called bronze, Stainless steel is made from 74% iron, 8 % carbon and 18 % chromium.
Distinguish between: (Two points of distinction)
Question 1.
Metals and Nonmetals.
Answer:
Metals:
- Metals have a lustre.
- They are generally good conductors of heat and electricity.
- They are generally solids at room temperature.
Exception: Mercury and gallium are liquids. - Metals form basic oxides.
Nonmetals:
- Nonmetals have no lustre.
Exception: Iodine and Diamond. - They are bad conductors of heat and electricity.
Exception: Graphite. - They are generally gases and solids at room temperature.
Exception: Bromine is a liquid. - Nonmetals form acidic or neutral oxides.
![]()
Question 2.
Roasting and Calcination.
Answer:
Roasting:
- In this process, the ore is heated strongly in the presence of air.
- In this process, sulphide ore is converted into metal oxide.
- During this process SO2 is given out.
Calcination:
- In this process, the ore is heated strongly in the limited supply of air.
- In this process, carbonate ore is converted into metal oxide.
- During this process CO2 is given out.
Give scientific reasons for the following:
Question 1.
Calcium floats on water during the reaction with water.
Answer:
- Calcium reacts with water less vigorously hence the heat evolved is not sufficient for hydrogen to catch fire.
- Instead, calcium floats on water because the bubbles of hydrogen gas formed stick to the surface of the metal.
Question 2.
Common salt has high melting and boiling points.
Answer:
- Common salt is an ionic compound. Common salt is solid and hard due to strong electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged Na+ and Cl- ions.
- A large amount of energy is required to break the strong intermolecular attraction (strong ionic bond). Hence, common salt has high melting and boiling points.
Question 3.
Metals are good conductors, while non-metals are poor conductors of electricity.
Answer:
- The electrons in the outermost orbit of atoms of a metal are free to move throughout the metal.
- When a potential difference is applied between the ends of a metal wire, the movement of the electrons constitutes an electric current. Hence, metals are good conductors of electricity.
- Nonmetals involve covalent bonding and do not have free electrons like metals. Hence, nonmetals are poor conductors of electricity.
Question 4.
Sodium is more reactive than aluminium.
Answer:
- If the number of electrons in the outermost orbit of an atom of a metal is less, the metal is more reactive.
- Sodium has electronic configuration (2, 8, 1) and aluminium has electronic configuration (2, 8, 3). The number of electrons in the outermost orbit of sodium and aluminium atoms are 1 and 3, respectively. Hence, sodium is more reactive than aluminium.
![]()
Question 5.
When zinc granules are added to copper sulphate solution, the blue coloured solution turns colourless.
Answer:
- Zinc is more reactive than copper.
- When zinc granules are added to copper sulphate solution, they displace copper from the copper sulphate solution to form zinc sulphate solution. As zinc sulphate is colourless, the blue coloured solution of copper sulphate disappears.
Question 6.
When an iron nail is dipped into a copper solution, a shiny coat of copper is formed on the nail.
Answer:
- Iron is more reactive than copper.
- When an iron nail is dipped into copper sulphate solution, iron displaces copper from the copper sulphate solution. The copper so liberated deposits on the iron nail. As a result, a shiny coat of copper is formed on the nail.
Question 7.
Cryolite (Na3AlF6) and fluorspar (CaF2) are added to the electrolytic mixture containing pure alumina.
Answer:
(1) Alumina has very high melting point ( > 2000 °C). Cryolite (Na3AlF6) and fluorspar (CaF2) lower the fusion temperature of the mixture containing alumina from 2000 ° C to 1000 ° C, thereby saving electrical energy.
(2) They increase the conductivity and the mobility of the fused mixture. Hence, cryolite and fluorspar are added to the electrolytic mixture containing pure alumina.
Question 8.
Air is bubbled through the mixture in Froth floatation process.
Answer:
(1) In the froth floatation process, in a tank water, ore and an oil are mixed. When air is bubbled through the mixture the oil forms froth.
(2) The mineral particles are wetted by the oil and float on the surface.
(3) The gangue particles are wetted by water and settle down. Hence, the ore can be concentrated. Hence, air is bubbled through the mixture in froth floatation process.
Question 9.
Silver amalgam is used for filling dental cavities.
Answer:
(1) Silver is a soft metal and wears off on constant usage particularly due to abrasion. Silver amalgam is an alloy of silver with mercury.
(2) It is a hard substance. It is nontoxic. Besides these properties it is a lustrous shining substance. It melts at a comparatively low temperature and can therefore conveniently fill in the cavities. Hence, silver amalgam is used for filling dental cavities.
Explain the following reactions with the help of balanced equations:
Question 1.
Out of sodium and sulphur which is a metal? Explain its reaction with oxygen. (March 2019)
Answer:
Sodium is a metal. Sodium reacts with oxygen in air at room temperature to form sodium oxide.
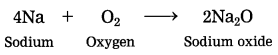
![]()
Question 2.
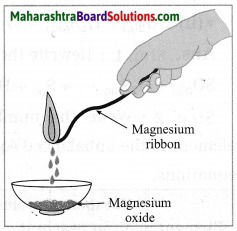
Magnesium burns in air.
Answer:
When magnesium bums in air, it combines with oxygen, emitting intense light and heat to form magnesium oxide.
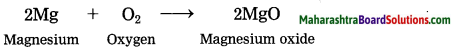
Question 3.
Copper reacts with air.
Answer:
Copper tarnishes in moist air and forms black coloured oxide when strongly heated.
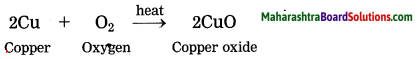
Question 4.
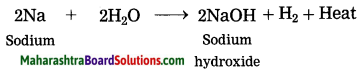
Sodium reacts with water.
Answer:
When sodium reacts with water, it evolves hydrogen which immediately catches fire producing a lot of heat.
Question 5.
Calcium reacts with water.
Answer:
Calcium reacts with water less vigorously to form hydrogen gas and calcium hydroxide. In this reaction, the heat evolved is not sufficient for hydrogen to catch fire.
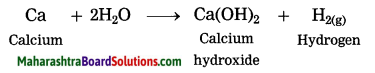
Question 6.
Steam is passed over aluminium.
Answer:
When steam is passed over aluminium, hydrogen gas and aluminium oxide are formed.
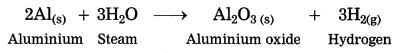
Question 7.
Steam is passed over iron.
Answer:
When steam is passed over iron, iron (III) oxide and hydrogen gas are formed.
![]()
Question 8.
Magnesium reacts with dil. hydrochloric acid.
Answer:
When magnesium reacts with dil. hydrochloric acid, magnesium chloride is formed and hydrogen gas is evolved.

Question 9.
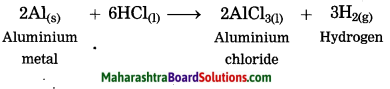
Aluminium is treated with dil. hydrochloric acid.
Answer:
When aluminium is treated with dil. hydrochloric acid, aluminium chloride and hydrogen gas are formed.
Question 10.
Zinc reacts with dil. hydrochloric acid.
Answer:
When zinc reacts with dil. hydrochloric acid, zinc chloride and hydrogen gas are formed.
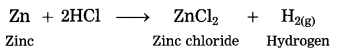
Question 11.
Iron is treated with dil. hydrochloric acid.
Answer:
When iron reacts with dil. hydrochloric acid, ferrous chloride and hydrogen gas is formed.

Question 12.
Copper is reacted with cone, nitric acid.
Answer:
When copper is reacted with cone, nitric acid, copper nitrate and reddish brown nitrogen dioxide are formed.

Question 13.
Copper is reacted with dil. nitric acid.
Answer:
When copper is reacted with dil. nitric acid, copper nitrate and nitric oxide are formed.
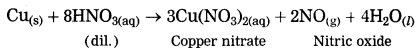
Question 14.
Sodium metal is reacted chlorine gas.
Answer:
When sodium metal is reacted with chlorine, sodium chloride an ionic compound is formed.
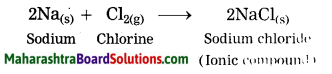
Question 15.
Sulphur burns in air.
Answer:
When sulphur burns in air, it combines with oxygen to form acidic sulphur dioxide.
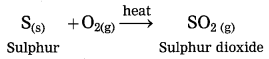
Question 16.
Chlorine dissolves in water.
Answer:
When chlorine dissolves in water, hypochlorous acid is formed.
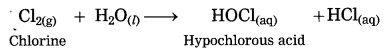
Question 17.
Chlorine is treated with hydrobromic acid.
Answer:
When chlorine is treated with hydrobromic acid, chlorine displaces bromine from hydrobromic acid.
Cl2(g) + 2HBr(aq) → 2HCl(aq) + Br2(aq)
Question 18.
Hydrogen gas is passed over boiling sulphur.
Answer:
When hydrogen gas is passed over boiling sulphur, sulphur combines with hydrogen to form hydrogen sulphide which has rotten egg smell.
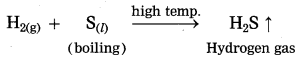
![]()
Question 19.
Sodium aluminate is treated with water.
Answer:
When sodium aluminate is treated with water, it is hydrolysed to give a precipitate of aluminium hydroxide.
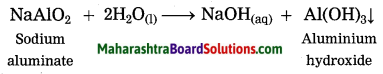
Question 20.
Dry aluminium hydroxide is ignited at 1000 °C.
Answer:
When dry aluminium hydroxide is ignited at 1000 °C, alumina (Al2O3) formed.
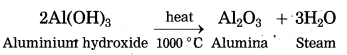
Question 21.
Zinc sulphide is heated strongly in excess of air.
Answer:
When zinc sulphide is heated strongly in excess of air, it forms zinc oxide and sulphur dioxide gas.
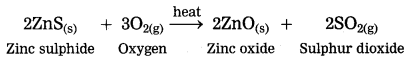
Question 22.
Zinc carbonate is heated strongly in a limited supply of air.
Answer:
When zinc carbonate is heated strongly in a limited supply of air, it gives zinc oxide and carbon dioxide.
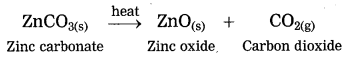
Question 23.
Zinc oxide is treated with carbon.
Answer:
When zinc oxide is treated with carbon, it is reduced to zinc. In this reaction, carbon acts as reducing agent.
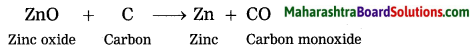
Question 24.
Manganese dioxide is heated with aluminium.
Answer:
When manganese dioxide is heated with aluminium, manganese dioxide is reduced to manganese and large amount of heat is evolved.
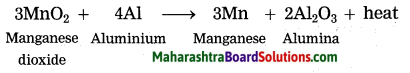
Question 25.
Cinnabar is heated in air.
Answer:
When cinnabar is heated in air, it forms mercuric oxide and sulphur dioxide.
Question 26.
Cuprous sulphide is heated in air.
Answer:
When cuprous sulphide is heated in air, cuprous oxide is formed. Cuprous oxide is reduced to copper in the presence of ore.
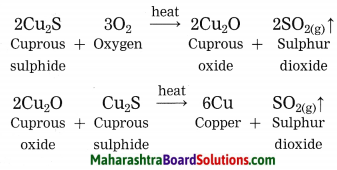
![]()
Project: (Do it your self)
Project 1.
Which metals are used in day to day life? What are its uses?
Project 2.
Which nonmetals are used in day to day life? What are its uses?