Balbharti Maharashtra State Board Class 7 English Solutions Chapter 1.4 The King’s Choice Notes, Textbook Exercise Important Questions and Answers.
Std 7 English Lesson 1.4 The King’s Choice Question Answer Maharashtra Board
Class 7 English Chapter 1.4 The King’s Choice Textbook Questions and Answers
1. Write a character sketch of each of the animals. Write about their actions and thoughts and the qualities that emerge through
Question 1.
Write a character sketch of each of the animals. Write about their actions and thoughts and the qualities that emerge through
Answer:
1. Lion: Lion was big and strong and very fierce. All the other animals in the forest called him king. The king promised other animals to give them food and protection. Whenever the king roared other animals stood in awe. Whenever he took a walk, others followed him. The lion was king also very responsible. When he had his meal, he left remains for other. So they always had enough to eat.
2. Fox: He was wise and clever creature and adviser of lion king. The fox took an oath of loyalty to the king.
3. Leopard: He was watchful and swift of foot, and a body of lion king.
4. Vulture: He was bird and can fly high in sky and a messager of lion.
![]()
2. Using your imagination, write more sentences in the same pattern:
(a) But the more the lion had, the more he wanted.
(b) Whenever he took a walk, they followed him.
(c) To be king is good. But to be kind is better.
Question a.
Using your imagination, write more sentences in the same pattern:
(a) But the more the lion had, the more he wanted.
(b) Whenever he took a walk, they followed him.
(c) To be king is good. But to be kind is better.
Answer:
- The more you quieten the mind, the more restless it becomes.
- Whenever I speak, he interrupts me.
- It is nice to be important. But it is more important to be nice.
- To live well on earth is good. But to leave well is better.
![]()
3. Turn the story into a play as a group activity and present the scenes in the classroom.
Question 1.
Turn the story into a play as a group activity and present the scenes in the classroom.
Answer:
(Curtain opens) The lion is seen pacing back and forth in deep thought.
- Lion: Hmmm, I think it’s time I’ve courtiers for myself. (Calls his guards.) Tell the fox, the leopard and the vulture to meet me at once.
- Guard: Yes, Your Majesty! (Enter of fox, leopard and the vulture)
- Fox, Leopard, Vulture: Our salute to the king of kings! (all bow down)
- Lion: Mr. Fox, you are known for your wisdom. You shall be my advisor from now on.
- Mr. Fox: (elated) As you wish, Your Majesty!
- Lion: And you…. Mr. Leopard, I am impressed by your alertness. You are swift of foot too. You shall be my bodyguard.
- Mr. Leopard: (humbly) I shall be happy to serve you, Your Majesty!
- Lion: (gesturing) And dear Vulture, you fly high above. I appoint you as my messenger.
- Mr. Vulture: I am honoured, Your Majesty! (One day the vulture enters all excited)
- Mr. Vulture: O great king! I have seen a camel in the desert not far away. I think it will be a good idea for you to taste camel meat.
- Lion: (looking at his other advisers) What do you say? (Mr. Fox & Mr. Leopard not wanting to show ignorance)
- Mr. Fox & Mr. Leopard: We don’t mind. But since the vulture has suggested let him lead the way. We shall humbly follow. (All set off on a journey to the forest. It’s hot and the sun is shining brightly.)
- King: Oh! It’s too hot to bear. My paws are burning.
- Mr. Vulture: (flying high above in cooler air) Your Majesty! The desert is close by. We shall reach in some time.
- King: (not able to bear the pain) Stop! We shall return.
- Mr. Vulture: (in thought) If we return, there will be nothing for us to eat as I will not be able to eat the king. I must stop him from returning. “Your Majesty! If you want we shall rest”.
- Mr. Fox: O king! We are far away from the forest. Let us continue towards the desert.
- King: I cannot walk anymore.
- Mr. Leopard: (thinking to himself) I wish I could run away from here.
- Fox: Let me ask for help, (leaps towards the desert)
(In the desert)…
![]()
4. This story takes an unexpected turn when the lion decides to spare the camel’s life. Choose any fable, story that you like and rewrite it giving it an unexpected turn.
Question 1.
This story takes an unexpected turn when the lion decides to spare the camel’s life. Choose any fable, story that you like and rewrite it giving it an unexpected turn.
Answer:
A ‘friend’ is a position in one’s heart and not the court. A courtier works for money. There is self-interest involved whereas a friend is a far more selfless relation in which one does not expect anything in return. It is a relationship in which friendship itself is the only reward.
5. Talk about the good qualities of any one person you do not like. (You need not name the person.)
Question 1.
Talk about the good qualities of any one person you do not like.
Answer:
I do not like my benchmate in my class as she is very untidy and comes shabbily dressed. However, there are many good qualities in her that I admire. She is an extremely polite girl. I have seen her go out of her way to help my other classmates. Also, she is very regular in her studies besides being a voracious reader. A habit that I long to imbibe in myself.
![]()
6. Language Study: Common nouns-i: Some things, animals, etc., that is, some nouns can be counted. They are called countable nouns. Some common nouns stand for something that cannot be counted. They are called uncountable nouns. Countable nouns have two forms. A noun that shows one person or thing, etc. is said to be in the singular. For example, ‘boy’, ‘girl’, ‘dog’, ‘tree’, ‘chair. A noun that shows more than one person or thing, etc. is said to be in the plural. For example, ‘boys’, ‘girls’, ‘dogs’, ‘trees’, ‘chairs’.
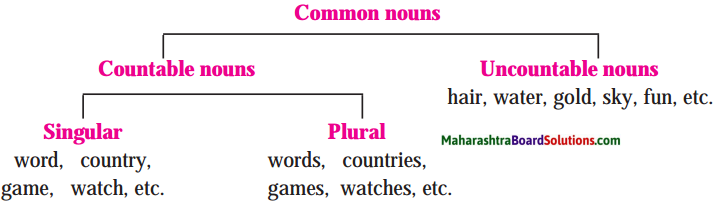
Note the expressions ‘a slice of bread’, ‘strands of hair’, ‘two glasses of water’, ‘a cup of milk’ and ‘a bit of fun!’. Here, we do not say ‘breads’, ‘hairs’, ‘waters’, ‘milks’, ‘funs’, etc.
Question 1.
Find five countable nouns from the passage and write their singular and plural forms.
Answer:
- life – lives
- friend – friends
- messenger – messengers
- gift – gifts
- creature – creatures
Question 2.
List the units that we use to measure the following: water, milk, distance, weight.
Answer:
- water – litres
- milk – litres
- distance – centimetre, metre, kilometre
- weight – grams, kilograms
Class 7 English Chapter 1.4 The King’s Choice Additional Important Questions and Answers
Answer the following questions:
Question 1.
What qualities are necessary in the following? Why?
Answer:
1. King: A king should be just and kind. His justice will instill faith towards him in his subjects and his kindness will help him win their hearts. A king should not demand respect instead it should be earned with his qualities and virtues.
2. Adviser: An adviser must be very wise and foresighted. He must weigh the pros and cons of a decision and only then advise the king to go ahead with it. This is also because once the decision is taken it cannot be reverted and fate of the entire kingdom largely depends on these decisions.
3. Bodyguard: A bodyguard of a king must be his shadow. Extremely vigilant and alert, the bodyguard should be able to sense trouble and mischief as the king’s life can be in danger if he lacks these qualities. He should not hesitate to risk his life to save the king if required. This also demands physical strength and spirit.
4. Messenger: A messenger should be very quick at carrying messages as sometimes the messages are so important and urgent that any loss of time may cause great harm to the kingdom. Moreover, the messenger should be very faithful and keep the messages of the king confidential. This will safeguard the kingdom from enemies. Also, the messenger should remember that he represents the king himself, hence should be very trustworthy.
![]()
Question 2.
Write the oath that each of the courtier must have taken.
Answer:
1. Oath taken by the advisor (Fox):
I, Mr. Fox, do hereby solemnly swear that I will remain loyal to my king and the kingdom and to the best of my ability advise the king on matters of administration in order to preserve, protect and defend the kingdom.
2. Oath taken by the messenger (Vulture):
I, Mr. Vulture, do hereby solemnly swear that I will remain loyal to my king and this great kingdom and will to the best of my ability deliver messages as and when required. In doing so I shall not alter the messages, keeping them confidential in the best interest of my kingdom in order to preserve, protect and defend it.
3. Oath taken by the bodyguard (Leopard):
I, Mr. Leopard, do hereby solemnly swear that I shall always be with the king like his shadow and will to the best of my ability protect, guard and defend the king and in doing so with loyalty I shall not hesitate to lay down my life in the general good of my beloved land.
Question 3.
Why was the vulture told to lead the way?
Answer:
The vulture had suggested that the lion should eat the camel it had seen in the desert. As, neither the lion nor the fox, nor the leopard had ever seen a camel and besides, as the fox and leopard didn’t want the vulture to appear wiser than them, they asked the vulture to lead as it was his idea.
![]()
Question 4.
Why had the lion never seen a camel?
Answer:
The lion stayed in the forest and a camel lives in a desert. So the lion had never seen a camel.
Question 5.
What advice did the fox and the leopard give? Was it based on good and sound thinking?
Answer:
The fox and the leopard advised the king to set off on a camel hunt. This advice was not based on good and sound thinking as they were accustomed to walking in the forest under shady trees and the desert would not provide them this comfort. They didn’t want to appear foolish and ignorant and so the advice.
Question 6.
Do you think the vulture was enjoying the search?
Answer:
Yes, as the vulture was flying high up in the cooler air, it was enjoying the search.
Question 7.
Do you think the king’s decision to go back was right?
Answer:
No, I don’t think the king’s decision to go back was right as he had already walked a long distance not only risking his life but that of his courtiers as well. He could have rested and then continued.
![]()
Question 8.
Can you guess the plan the fox had thought of?
Answer:
The fox had planned to trick the camel, and use him as a means of transport to go to their forest, kill him and have a feast.
Question 9.
Why does the fox address the camel as friend camel?
Answer:
The fox addressed the camel as ‘friend camel’ to make him believe that he is his well-wisher so that the camel does not see through his wicked intentions.
Question 10.
What qualities of the courtiers emerge in this part of the story when they were in the desert?
Answer:
The lion king comes across as someone who had leapt before looking what he was landing into. He himself didn’t know how he would return to the forest but commanded that they should stop right there. Not a very thoughtful and far sighted king. The vulture appears to be self-centred and greedy. He was only interested in eating the camel. The leopard, though a bodyguard, was a coward who wanted to run away. However, the fox comes across as a problem-solver who rescues everyone from the situation with his wit.
Question 11.
The fox, the leopard and the vulture have the same thought about the camel. Why is it so?
Answer:
By sparing the camel and not eating it, the king had spoilt the plan of the fox, vulture and the leopard. As they had similar interests, they had the same thought about the camel. The animals were all tired and hungry and realised that the camel would make a large meal. The camel being simple minded would not suspect this play and they could easily have a feast and satiate their hunger by fooling him. They were now irritated with their plans having been failed.
![]()
Question 12.
Did you expect the lion to be kind to the camel? Do you think his decision was right?
Answer:
No, I didn’t expect the lion to be kind to the camel who was his prey. Yes, I think the lion’s decision was right as he was thankful to the camel for saving their lives by carrying them back to the forest. His decision was a mark of gratitude towards the camel.
Answer in one sentence.
Question 1.
Why did the king appoint the leopard as his bodyguard?
Answer:
The king appointed the leopard as his bodyguard as he was watchful and swift on his feet.
Question 2.
What did the lion’s courtiers do when he went hunting?
Answer:
When the lion king went hunting, the courtiers found animals for him to kill.
Question 3.
How does the vulture describe the camel to the lion king?
Answer:
The vulture describes the camel as a lone animal in the desert who was big and fat.
Question 4.
Why couldn’t the lion walk any further?
Answer:
The lion could not walk any further as the hot sand had burned his paws.
![]()
Question 5.
What does the fox tell the camel?
Answer:
The fox tells that the camel that the lion king had killed his master and it was now free. The lion king, therefore, had invited it to live at his court.
Question 6.
On what condition did the camel agree to serve the lion?
Answer:
The camel agreed to serve the lion in return for a home at his court.
Question 7.
Why were the courtiers shocked to listen to the lion king’s decision?
Answer:
The courtiers were shocked to listen to the lion king’s decision as they had risked their lives to eat the camel’s meat but the king had now decided to spare it.
Reading Skills, Vocabulary and Grammar
Read the following passage and do the activities.
Simple Factual Questions:
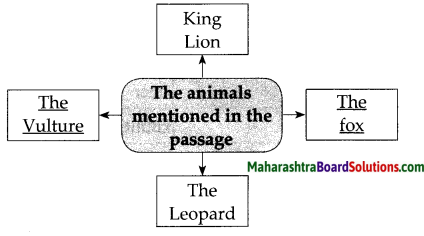
Question 1.
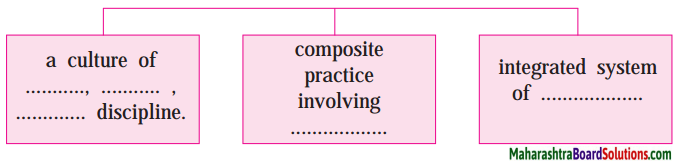
Complete the web
Answer:
Question 2.
Who said to whom
Question i.
“A king must have a court”
Answer:
The king thought to himself.
![]()
Question ii.
“I want you to be my adviser”
Answer:
The king said the above sentence to the fox.
Question iii.
“I want you to be my bodyguard”
Answer:
The king said the above sentence to the leopard.
Question iv.
“You are to be my messenger”
Answer:
The king said the above sentence to the vulture.
Complex Factual Questions:
Question 1.
Why must a king have a court?
Answer:
A king must have a court for the smooth functioning of his kingdom. Besides, the king cannot do everything on his own so, by delegating work to his courtiers, the king can assure that various departments in his kingdom are serving his subjects well.
Question 2.
How is the human administration similar to that of what we read in the passage?
Answer:
Just as we have different portfolios the Lion king also gave responsibilities to his courtiers. For example the fox who is very wise and clever and we too have a council of ministers who advice the Prime Minister; just like the leopard who is watchful and swift, we too have the defence system in our country and like their vulture who is a messenger we too have the ministry of communication and technology.
![]()
Question 3.
What is the oath of loyalty?
Answer:
An oath of loyalty is a pledge one takes acknowledging one’s duty and faithfulness towards one’s country or a king.
Vocabulary:
Question 1.
Give the meanings of the following words.
Answer:
- courtiers – people who attend the royal court
- adviser – the one who advises
- bodyguard – a person employed to protect somebody
- loyal – faithful towards a person or an organisation.
Grammar:
Question 1.
Pick out the Subject and Predicate from the following sentences.
1. They brought him gifts from every corner of the forest.
2. The lion called a leopard to his side.
3. The fox, the vulture and the leopard took an oath of loyalty to the king.
4. The three courtiers never opposed the king.
Answer:
| Subject | Predicate |
| 1. They | brought him gifts from every corner of the forest. |
| 2. The lion | called a leopard to his side. |
| 3. The fox, the vulture and the leopard | took an oath of loyalty to the king. |
| 4. The three courtiers | never opposed the king. |
![]()
Question 2.
Identify any 4 common nouns from the above passage.
Answer:
king, forest, fox, leopard, animals
Question 3.
Add the question tag for the following sentences.
- He called a fox to his side.
- You are to be my messenger.
- The king promised to give them food and protection.
- He was big and strong and very fierce.
Answer:
- He called a fox to his side, didn’t he?
- You are to be my messenger, aren’t you?
- The king promised to give them food and protection, didn’t he?
- He was big and strong and very fierce, wasn’t he?
Question 4.
Give the adjective forms for the following.
- protection
- loyalty
- watch
- thought
Answer:
- protective, protected
- loyal
- watchful
- thoughtful
![]()
Question 5.
Complete the table using the singular or plural forms of the nouns.
Answer:
| Singular | Plural |
| 1. apple | apples |
| 2. book | books |
| 3. class | classes |
| 4. photo | photos |
| 5. life | lives |
| 6. woman | women |
| 7. mouse | mice |
| 8. child | children |
| 9. deer | deer |
| 10. country | countries |
![]()
Question 6.
Find five countable nouns from the passage and write their singular and plural forms.
Answer:
| Singular | Plural |
| 1. king | kings |
| 2. animal | animals |
| 3. gift | gifts |
| 4. fox | foxes |
| 5. bird | birds |
Read the following passage and do the activities.
Simple Factual Questions:
Question 1.
State whether the following statements are true or false.
1. The lion ordered his courtiers to eat the camel.
2. The vulture, fox and the leopard offer themselves to the lion king.
Answer:
1. False
2. True
Complex Factual Questions:
Question 1.
Were the courtiers being loyal to their king?
Answer:
No, the courtiers were not being loyal to their king as by getting the camel killed by the lion they would force the lion king to go against his own promise of protecting the camel thereby spoiling the king’s image.
Question 2.
What qualities of the camel are seen in his speech?
Answer:
The camel comes across as very humble and loyal character. He knows very well that he could not be of much use to the lion in the forest. Moreover, he is willing to lay down his life for the sake of his king which means that he is extremely selfless.
![]()
Question 3.
Why did the lion laugh to see the courtiers go?
Answer:
The lion laughed to see the courtiers go because he knew they were unfaithful courtiers and were only with him to serve their own selfish motives. He had been successful in driving them away without pronouncing a cruel judgment against them.
Question 4.
Why did the king offer his friendship to the camel?
Answer:
The king realized that his courtiers were unfaithful. In contrast, the camel was loyal and good. So, he offered friendship to the camel.
Question 5.
Explain the lines “To be king is good. But to be kind is better”.
Answer:
The king through the lines “To be king is good, but to be kind is better” wants to say that as a king he demanded respect but couldn’t win loyal friends or courtiers. But by being kind to the camel he not only gained respect but also won a true friend.
Vocabulary:
Question
Give homophones for the following words.
(a) accept
(b) seen
Answer:
(a) except
(b) scene
![]()
Grammar:
Question 2.
Away flew the vulture.
(Separate the subject and predicate.)
Answer:
The vulture – subject, flew away – predicate
Question 3.
They were never seen in the forest again.
(Add a question tag)
Answer:
They were never seen in the forest again, were they?
Question 4.
What qualities of the lion king impresses you the most? Why?
Answer:
The lion king was very witty and wise. He had the skill of teaching his wicked and cunning courtiers a lesson without being cruel to them. He also had the quality of distinguishing between the faithful and the unfaithful. These qualities of the lion king impress me the most.
Language Study:
Do as directed.
Question 1.
The king promised to give them food and protection. (Rewrite using ‘Not only… but also’.)
Answer:
The king promised to give them not only food but also protection. The king not only promised to give them food, but also protection.
Question 2.
Let us go back to the forest.
(State the kind of sentence.)
Answer:
Imperative sentence.
![]()
Question 3.
They did not want the vulture to seem wiser than them. (Iden tify the degree of comparison.)
Answer:
Comparative degree.
Question 4.
All the other animals in the forest called him king.
(Rewrite beginning with ‘He was’.)
Answer:
He was called king by all the other animals in the forest.
Question 5.
“Our king, the lion, has killed your master” said the fox.
(Change into indirect speech.)
Answer:
The fox informed that their king, the lion, had killed his master.
![]()
Question 6.
Make sentences using phrases/idioms.
Answer:
- To set off – We packed our bags and set off on a nature trail.
- To keep (yourself) from – My grandmother is 70 years old. But that does not keep her from enjoying treks.
Question 7.
Complete the table.
Answer:
| Noun | Verb | Adjective |
| friendship | befriend | friendly |
| life | live | lively |
| thought | think | thoughtful |
| protection | protect | protective |
| strength | strengthen | strong |
![]()
Writing Skills:
Question 1.
Choose any fable, story that you like and rewrite it giving it an unexpected turn.
Answer:
The Thirsts Crow
One hot day, a thirsty crow flew all across the plains in search of water. It had taken him more time than he thought and he felt weak. Losing all hope, he flew down to see if there was water kept outside the houses by the lonely street.
To his delight, he found a jug with water outside a small hut. But, the jug had very little water and it’s neck was too narrow for his head to be put in. He tried picking up the jug but in vain. Finally, he saw some pebbles and decided that if he dropped the pebbles, into the jug the water level would rise and he would be able to quench his thirst. But the crow had no patience to throw each pebble in one by one and wait for water level to rise slowly.
He saw a big stone lying by the side of the jug. He thought to himself, “if I put this big stone inside the jug, the level of water will rise at once”.
In his heart he felt proud about himself for this brilliant idea. So in desperation, he took the big stone and threw it in the jug. But to his disappointment, the stone hit the base of the earthen jug so hard that the jug broke into pieces. All the water from the jug spread all over the place. The crow tried to drink but before he could do so the thirsty earth had soaked in most of it.
Moral: Haste makes waste.
The King’s Choice Summary in English
The folk tale ‘The King’s Choice’ highlights the importance of virtues such as loyalty and kindness. The lion king in the story proves that a king’s might and majesty may win him some untrue and fake followers but kindness alone can give him the gift of faithful friends. On the other hand, the faithful camel’s character underlines the age old maxim, ‘Loyalty always pays’.
Paraphrase:
The story takes us to a forest where the lion king appoints the fox, the vulture and the leopard as his courtiers. However, the vulture due to his selfish and greedy motive of eating up the lion king lures him into going to the desert to eat camel meat. Other courtiers also follow.
When the king and his companions get tired of walking in the scorching sun, the fox comes to their rescue. He, through his wit and craftiness, befriends the camel and tricks him into believing that the king wanted to befriend him. The innocent camel appears before the king and carries the trio back to the forest on his back.
Filled with gratitude towards the camel on saving his life, the king decides to spare him and gives him his protection. Although the three courtiers are unhappy with the decision, they keep quiet.
However, after few days, unable to go hunting, the lion summons his courtiers and orders them to bring him food. The cunning fox once again holds a meeting and they plan to compel the king to eat the camel. But there is a twist in the story, the camel is safe once again due to its loyalty and the betrayers are compelled to flee. Thus, the king outsmarts his crafty and unfaithful courtiers and repays the camel for his loyalty with his kindness.
![]()
Glossary:
- fierce (adj) – physically violent and frightening
- swift (adj) – quick
- watchful (adj) – alert and vigilant
- oath (n) – promise or vow
- awe (n) – respect and fear
- remains (n) – the parts left over after other parts have been removed
- lone (adj) – only one
- vulture (n) – a large bird of prey
- paws (n) – an animal’s foot
- feast (n) – a large meal, typically eaten during celebrations
- risked (v) – put in danger
- grateful (adj) – thankful
7th Std English Balbharati Textbook Solutions
- Past, Present, Future Class 7 English Textbook Solutions
- Odd One In Class 7 English Textbook Solutions
- In Time of Silver Rain Class 7 English Textbook Solutions
- The King’s Choice Class 7 English Textbook Solutions
- Seeing Eyes Helping Hands Class 7 English Textbook Solutions
- A Collage Class 7 English Textbook Solutions